Are you dealing with the constant pain and stiffness of ankylosing spondylitis (AS)? You’re not alone. This chronic condition can really affect your life, but there’s hope. The right treatment can help manage your symptoms and prevent worse problems. In this guide, we’ll look at the effective treatment options for ankylosing spondylitis. This will help you take charge of your health and find relief.
Key Takeaways
- Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic arthritis that mainly affects the spine. It causes pain, stiffness, and less movement.
- Even though there’s no cure for AS, there are treatments to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Medicines like NSAIDs, DMARDs, and biologics like TNF and IL-17 inhibitors can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical therapy, exercise, and making lifestyle changes are key. They help keep joints moving, improve posture, and boost overall health.
- In serious cases, surgery might be needed to fix spinal deformities or joint damage.
Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis
Causes and Symptoms
Ankylosing spondylitis is an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic inflammation in the spine and other joints. The exact ankylosing spondylitis causes are not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to genetic factors and the body’s immune system attacking its own tissues. Symptoms commonly include back pain and stiffness, particularly in the morning and after periods of inactivity, as well as reduced spinal mobility and flexibility. In some cases, the condition can also affect other joints, such as the hips, knees, and ankles, and cause inflammation in the eyes, bowel, and other organs.
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis typically involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and blood tests. During the physical exam, healthcare providers may assess the range of motion in the spine and check for signs of inflammation. Imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, can reveal changes in the joints and bones that are characteristic of the condition. Blood tests may be used to check for the presence of the HLA-B27 gene, which is commonly found in people with ankylosing spondylitis, although its absence does not rule out the diagnosis.
“Seek medical attention if low back or buttock pain worsens in the morning, improves with exercise, and worsens with rest.”
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis and preventing the progression of the condition. Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential for individuals with this chronic condition.
| Ankylosing Spondylitis Statistics | Value |
|---|---|
| Prevalence in the US | 1.7 million adults |
| Prevalence of axial spondyloarthritis | 3.2 million adults |
| HLA-B27 prevalence in Caucasians with AS | Over 95% |
| Onset of symptoms | Late adolescence or early adulthood |
| Risk of inflammatory bowel disease | Up to 50% |
| Risk of acute anterior uveitis | 25%-35% |
Medications for Ankylosing Spondylitis
People with ankylosing spondylitis need different medicines to control pain, inflammation, and disease progress. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often the first choice. They help ease symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis.
NSAIDs and Pain Relievers
NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve) can reduce pain and inflammation. But, long-term use may lead to stomach problems and bleeding. Doctors might also give other pain medicines, like acetaminophen or codeine, to help with NSAIDs.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
Doctors may also prescribe DMARDs to manage symptoms. Medicines like sulfasalazine and methotrexate can lower inflammation and slow disease progress. But, they work better for other types of arthritis than spinal arthritis. Side effects can include headaches, stomach issues, and mouth ulcers.
Biologics, like TNF-α inhibitors and IL-17 inhibitors, are advanced treatments for those not helped by usual medicines. These drugs target specific inflammation pathways in ankylosing spondylitis. But, they can increase the risk of infections and certain cancers.
Choosing the right medicine for ankylosing spondylitis depends on the patient’s needs. This includes how severe symptoms are, how fast the disease is progressing, and the risks and benefits of each medicine. Regular check-ups and talking to a healthcare provider are key to finding the best treatment.
Biologic Treatments
When NSAIDs and traditional DMARDs don’t work for ankylosing spondylitis, doctors might try biologic meds next. These are special drugs that can help manage symptoms better.
TNF Inhibitors
TNF inhibitors are a common choice for ankylosing spondylitis treatment. They include drugs like adalimumab (Humira) and etanercept (Enbrel). These drugs block a protein that causes inflammation. Research shows they can greatly reduce pain and stiffness in people with ankylosing spondylitis.
IL-17 Inhibitors
IL-17 inhibitors, like secukinumab (Cosentyx), are another option. They block the IL-17 cytokine, which is involved in inflammation. These drugs are effective for those who don’t respond well to TNF inhibitors or can’t take them.
Dr. Robert Koval says biologic meds aim to clear up symptoms completely. While they can cause side effects, like infections, they are generally safe and well-tolerated by most people with ankylosing spondylitis.
“Approximately 8 out of every 10 people are expected to have a meaningful response to biologic therapy for ankylosing spondylitis.”
Doctors follow national guidelines when choosing biologic treatments for ankylosing spondylitis. This ensures the drugs are used wisely and for the patient’s best benefit.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Ankylosing spondylitis needs a mix of treatments, and physical therapy and exercise are key. Working with a physical therapist helps create a plan that keeps muscles flexible and strong. This plan also improves posture and supports the spine.
Studies show that exercise helps manage ankylosing spondylitis symptoms. One study found a 21% pain reduction in those who exercised. Another study showed moderate exercise can boost mobility and reduce disease activity.
The exercise plan for ankylosing spondylitis includes stretching, cardio, strengthening, and balance exercises. These are vital for better flexibility, less pain, and stronger muscles. They also help maintain good posture.
- Range of motion exercises improve flexibility and reduce stiffness and pain.
- Aerobic exercises boost heart and lung health, endurance, and mood.
- Strengthening exercises, especially for the core, support posture and manage back pain.
- Balance exercises enhance stability and reduce falling risks, important for those with lower bone density.
Regular exercise, for 20 minutes a day, can greatly improve symptoms. Working with a physical therapist helps create a tailored plan. This plan addresses specific needs and manages symptoms effectively.
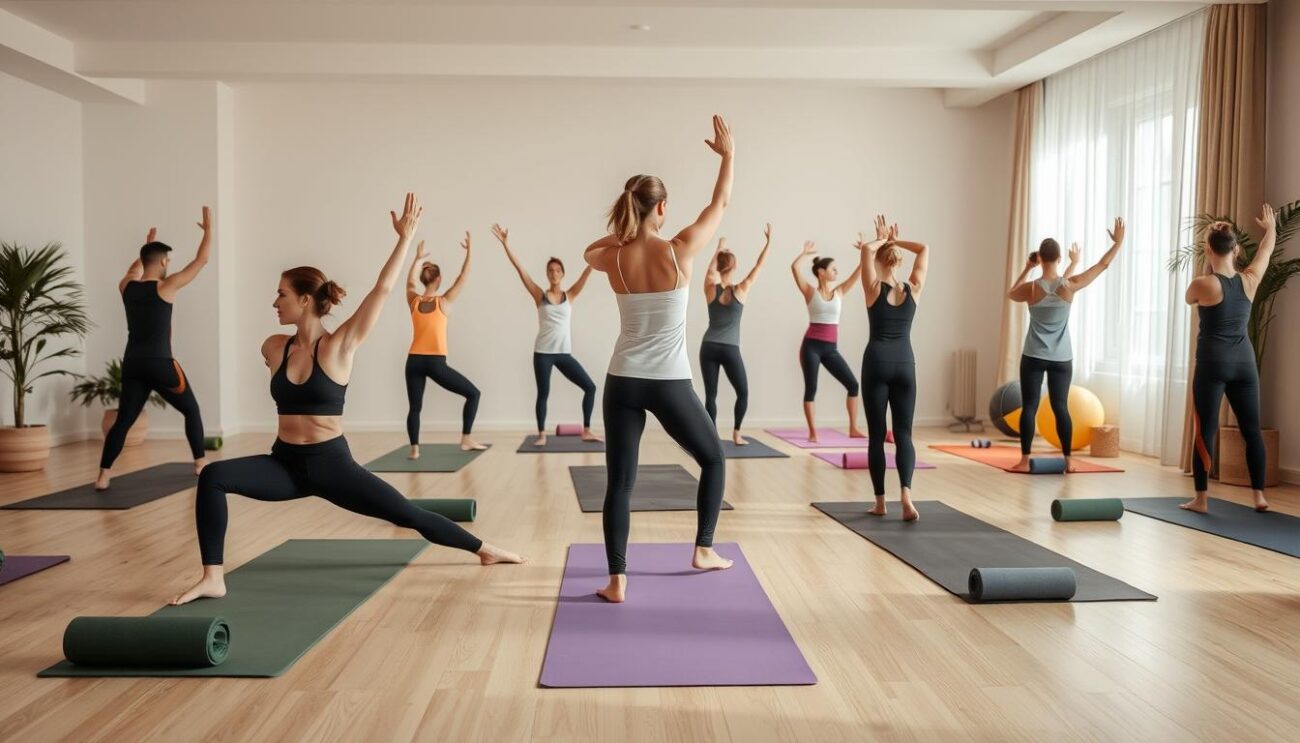

“Exercise is considered a crucial component of treating spondyloarthritis, with a holistic approach that includes exercise and wellness practices being the gold standard.”
Treatment Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis mainly affects the spine and sacroiliac joints. The main goals of ankylosing spondylitis treatment are to lessen pain and swelling. It also aims to keep or improve spinal movement and prevent deformities.
Treatment usually combines medicines, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. The right plan depends on how severe the symptoms are and how well the person responds to treatments.
Let’s look at the different ways to treat ankylosing spondylitis:
Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs, like ibuprofen and naproxen, are often the first choice. They help reduce swelling and ease pain.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Medications such as methotrexate and sulfasalazine can slow the disease’s progress. They also lessen symptoms.
- Biologic Agents: New biologic drugs, like TNF inhibitors (e.g., adalimumab, infliximab) and IL-17 inhibitors (e.g., secukinumab), work well against ankylosing spondylitis.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy is key in managing ankylosing spondylitis. Exercises and stretches help keep flexibility and posture good. Regular activities like swimming, walking, and low-impact exercises are also important.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle can help manage ankylosing spondylitis symptoms. This includes staying at a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and keeping good posture. Stress-reducing activities, like meditation or mindfulness, can also help.
In severe cases, surgical interventions might be needed. This could be for joint replacement or spinal fusion.
The best ankylosing spondylitis treatment involves a team effort. Working with healthcare professionals helps manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle can help with ankylosing spondylitis symptoms. Keeping a good posture is key to avoid spinal deformities. Doing low-impact exercises like swimming or walking can also help.
It’s crucial to talk to a healthcare provider about your exercise plan. They can make sure it’s safe and right for you.
Eating well is also important. There’s no special ankylosing spondylitis diet to cure it. But, eating healthy can help your joints and spine. Some people find that avoiding inflammatory foods and eating more anti-inflammatory foods helps.
Posture and Activity
- Maintain good posture, both when sitting and standing, to prevent further spinal deformities.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or walking, to maintain flexibility and reduce pain.
- Work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a safe and effective exercise plan.
Diet and Weight Management
There’s no special ankylosing spondylitis treatment diet. But, eating healthy can help your joints and spine. Some people find that avoiding inflammatory foods and eating more anti-inflammatory foods helps.
“Studies have shown benefits of long-term physical activity for people with AS, such as decreasing pain and improving sleep quality.”
By making lifestyle changes, like good posture, regular exercise, and a healthy diet, you can help manage ankylosing spondylitis symptoms. These changes can work alongside medical treatments.
Surgical Interventions
In most cases, surgery is not needed for ankylosing spondylitis. But, in severe cases, surgery might be suggested. This could be to replace a damaged hip or fix spinal deformities. Doctors decide on surgery based on each patient’s needs.
Surgery is for those with severe pain, lost mobility, or a poor quality of life. The surgery type depends on the condition’s impact. It could be for pain relief, spine stability, or better mobility.
- Laminectomy: A procedure that removes a portion of the vertebral bone to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots.
- Spinal fusion: This surgery fuses two or more vertebrae together to provide stability and reduce pain.
- Spinal osteotomy: A surgical procedure that reshapes and realigns the spine to improve posture and mobility.
- Hip joint replacement: In cases of severe hip joint damage, a total hip replacement may be necessary to alleviate pain and restore function.
Recovery from ankylosing spondylitis surgery can take weeks to months. Newer, less invasive techniques have made surgery safer and more effective.
“Surgery for ankylosing spondylitis is reserved for severe cases to relieve its effects.”
The cost of ankylosing spondylitis surgeries varies a lot. It can be from $11,000 to $37,000, depending on the surgery and medical needs. Patients should talk to their doctors about the benefits, risks, and costs to decide the best treatment.
Coping and Support
Living with ankylosing spondylitis is tough, both in body and mind. It’s key for those with this condition to find support and learn to cope. Joining a support group, online or in-person, is a great way to connect with others who get it.
Healthcare providers are also vital in helping manage the emotional side of ankylosing spondylitis. They can refer you to mental health services or offer tips on stress relief. Techniques like meditation or deep breathing can help ease chronic pain and fatigue.
Changing your lifestyle can also help. Eating well and exercising regularly can improve your overall health. By managing ankylosing spondylitis in a holistic way, you can adapt and thrive despite its challenges.
“The key to coping with ankylosing spondylitis is finding a balance between managing the physical symptoms and nurturing your emotional well-being. With the right support and strategies, you can learn to live life to the fullest.”
Remember, getting support and finding effective coping strategies are crucial. They help maintain a good quality of life and manage the long-term effects of ankylosing spondylitis.
Conclusion
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic condition without a cure. But, managing it has gotten much better in recent years. A mix of targeted medicines, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery helps a lot.
Working closely with doctors, people can create treatment plans that fit their needs. Thanks to treatments like NSAIDs, DMARDs, and biologic therapies, many live better lives. These treatments help control symptoms and slow the disease’s progress.
Being proactive in managing ankylosing spondylitis is key. This includes staying active, keeping a healthy weight, and adjusting daily habits. These steps help reduce the disease’s effects. With ongoing research, the future looks bright for those with ankylosing spondylitis.