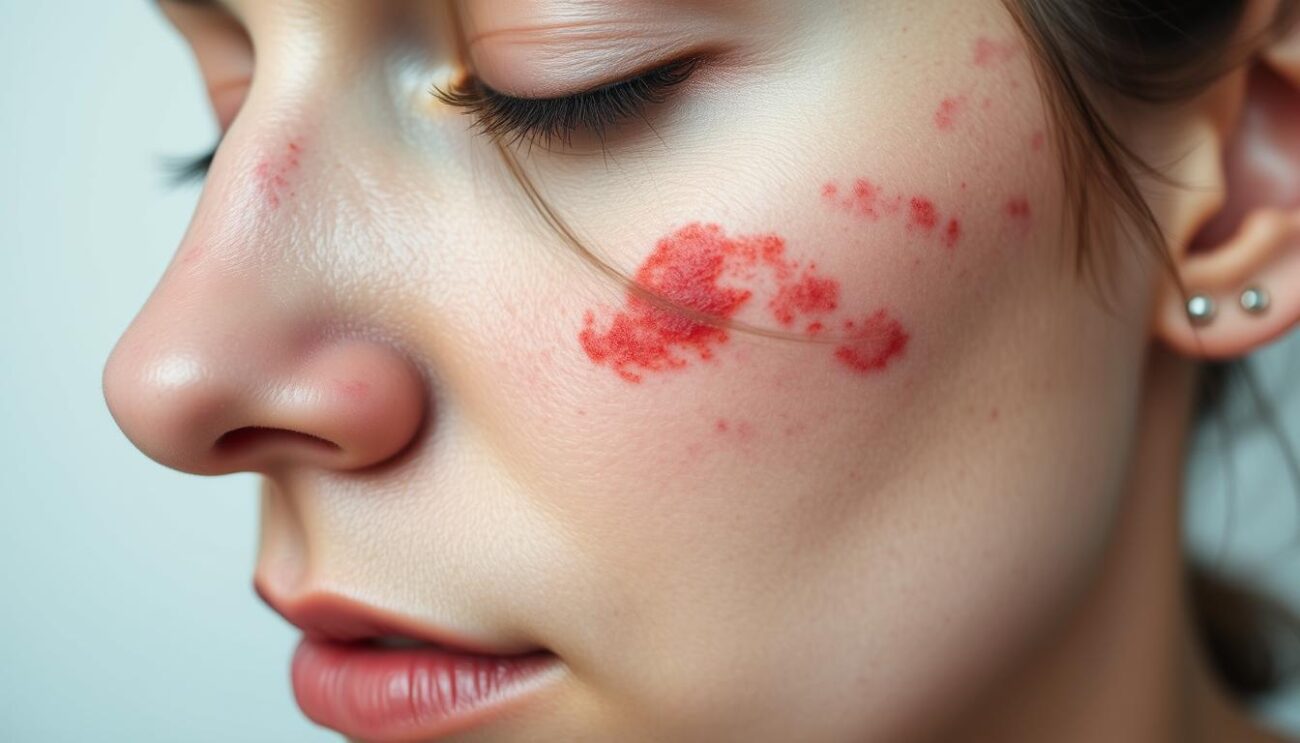
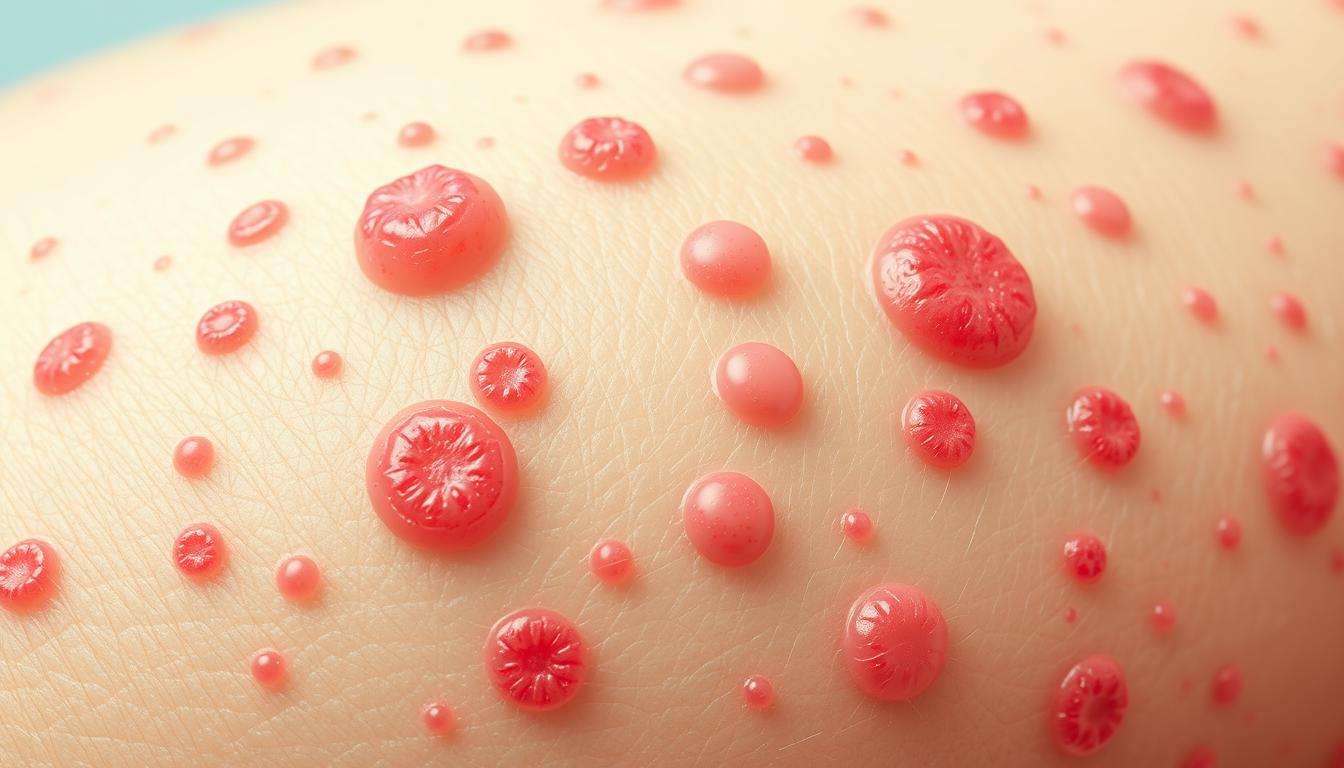
What if the skin rashes that disrupt your life could be solved by finding the cause? Chronic hives, or chronic urticaria, are common and frustrating. They are itchy welts that last for months or years. Finding out what causes them is the first step to feeling better.
Chronic hives are welts that last over six weeks and come back often. They can make it hard to sleep and do daily things, causing a lot of discomfort. The welts can be different sizes, shapes, and colors, depending on your skin tone.
Key Takeaways
- Chronic hives are a persistent skin condition characterized by recurring, itchy welts that can last for months or years.
- Understanding the potential causes and triggers of chronic hives is crucial for effective management and relief.
- Chronic hives can be caused by the release of immune system chemicals like histamine, and may be triggered by environmental factors or underlying medical conditions.
- Identifying and avoiding known triggers is an important step in managing chronic hives.
- Seeking medical attention is recommended for individuals experiencing persistent or unexplained hives.
Overview of Chronic Hives
Definition and Symptoms
Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, are itchy welts that last over six weeks. They can be red, purple, or skin-colored and vary in size and shape. These welts often appear on different parts of the body.
They can also cause painful swelling, known as angioedema. This swelling can happen around the eyes, cheeks, or lips.
Prevalence and Demographics
About 1.4% of people suffer from chronic hives. Women are more likely to get them than men, with a ratio of two to one. The condition is most common in adults aged 40 to 59.
It is also more common in Black Americans and other ethnic groups than in white people.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Chronic urticaria prevalence | 0.23% of the population |
| Age group with highest prevalence | 40-59 years |
| Gender distribution | Women affected twice as often as men |
| Ethnic group with higher prevalence | Black Americans and other ethnic groups |
“Chronic urticaria can last from 6 weeks to several years, with symptoms recurring periodically over an extended period.”
Potential Triggers and Causes
Finding the exact cause of chronic hives can be tough. But, there are several things that might lead to it. Knowing these can help manage and treat this skin issue.
Environmental Factors
Many environmental factors can start chronic hives. Heat, cold, and sunlight can all be triggers. Also, things like vibration, pressure, and friction can cause hives to flare up. Staying away from these environmental factors is key to controlling chronic hives.
Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions can lead to chronic hives. These include thyroid problems, infections, allergies, and even some cancers. Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and celiac disease also raise the risk of chronic hives. Treating these health issues might help ease chronic hives symptoms.
The causes of chronic hives are often complex. By knowing the environmental triggers and medical conditions involved, people can work with their doctors. Together, they can create a treatment plan to help manage chronic hives symptoms.
Autoimmune Disorders and Chronic Hives
Autoimmune disorders are linked to chronic hives. The body’s immune system can attack its own tissues. This leads to the release of histamine, causing itchy welts.
Conditions like thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus can cause chronic hives. This shows why it’s key to check for autoimmune factors when diagnosing this skin issue.
About 30% to 50% of idiopathic hives are caused by the body’s immune system. This is known as autoimmune hives. People with these hives might also have other autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune thyroid diseases, like Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, can sometimes cause hives.
Chronic hives last more than 6 weeks. Some people have them for years. Non-drowsy antihistamines can help by blocking histamine release.
But, if over-the-counter options don’t work, prescription meds like omalizumab or cyclosporine might be needed.
For autoimmune disorders chronic hives, treatments include the autoimmune protocol diet and acupuncture. Stress reduction, calamine lotion, and cool showers can also help. Avoiding tight clothes is important too.
If hives are caused by an allergen, remove it right away. See a doctor if hives last more than 6 weeks.
“Around 30% of people with chronic spontaneous urticaria also have Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune disorder affecting the thyroid gland.”
Food Allergies and Chronic Hives
Many people think food allergies cause chronic hives, but research shows this isn’t true for most. Only a small number of cases are linked to food allergies. Still, it’s key for those with chronic hives to check with their doctors about food triggers. These can differ from person to person.
A study by Sánchez, Sánchez, and Cardona in 2018 looked at food and chronic hives. They found a link between what we eat and how bad symptoms get. A 2019 review by Cornillier et al. also showed diet’s big impact on chronic hives.
Even if food allergies aren’t the main cause, diet can still affect chronic hives. Some foods might set off an immune reaction, making hives worse. Working with a doctor, people with chronic hives can find and avoid these foods. This might help manage their condition better.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Percentage of people who experience hives at some point in their lives | About 20% |
| Percentage of acute hives cases in children caused by viral infections | More than 80% |
| Percentage of people with chronic hives who are hive-free within one year | Almost 50% |
Even though food allergies aren’t a common cause, it’s still crucial for those with chronic hives to explore dietary factors. A full approach to managing chronic hives can greatly improve life quality. It helps control the condition better.
Stress and Chronic Hives Causes
Stress and hormonal imbalances can lead to chronic hives. Stress can cause the body to release hormones and chemicals. These can cause the skin reactions seen in chronic hives. Hormonal changes, like those in pregnancy or menopause, can also trigger or make chronic hives worse.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances are key in chronic hives. Stress, age, and health issues can cause these imbalances. This is important to know for treating chronic hives.
- Stress can release hormones like cortisol, leading to inflammation and hives.
- Hormonal changes in big life events, like pregnancy or menopause, can start or make hives worse.
- Hormonal issues can mess with the immune system. This can lead to too much histamine and hives.
Managing stress and hormones is key to dealing with chronic hives. Working with doctors to find the cause can help find relief.
“Chronic hives can greatly affect a person’s life. It can mess with daily activities, sleep, and mood. Knowing how stress and hormones play a part is vital for managing it.”
Chronic Hives Causes
Many people with chronic hives, also known as chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) or chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), struggle to find the cause. This condition, where the cause is unknown, is called idiopathic urticaria. Researchers are working hard to find the reasons behind this condition. They aim to improve how doctors diagnose and treat it.
Chronic hives can really disrupt daily life, lasting for a long time. Even though the exact cause is often unknown, experts have found some possible reasons. These include autoimmune disorders, food allergies, stress, and other health issues. Understanding idiopathic urticaria is key to finding better ways to manage it.
Unraveling the Causes of Idiopathic Urticaria
When the cause of chronic hives is not found, it’s called idiopathic urticaria. This means the reason for the skin reactions is still a mystery. Researchers are looking into many possible factors that might cause chronic spontaneous urticaria. These include:
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like thyroid dysfunction, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis may be linked to chronic hives.
- Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections can sometimes trigger the release of histamines and lead to hives.
- Stress and hormonal imbalances: Emotional stress and changes in hormones can disrupt the body’s inflammatory response and contribute to chronic hives.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, medications, or other environmental triggers may play a role in some cases of idiopathic urticaria.
By studying these factors, researchers hope to find better ways to diagnose and treat chronic, idiopathic urticaria.
“The underlying cause of chronic hives often remains a mystery, but understanding the potential contributing factors is key to finding effective management solutions for those affected by this persistent skin condition.”
Angioedema and Chronic Hives
Chronic hives are a skin condition that causes long-lasting rashes and itching. Sometimes, they come with angioedema, which makes the skin swell deeper. This swelling often happens around the eyes, cheeks, or lips.
Angioedema is caused by chemicals like histamine. These chemicals make fluid build up and cause inflammation. This can make the skin swell.
About 50% of people with chronic hives who don’t get better with antihistamines might need omalizumab. This treatment can help with both conditions.
Many things can trigger angioedema, like certain medicines and foods. Foods like shellfish, fish, peanuts, and tree nuts can cause it. Severe swelling in the tongue or throat is very dangerous and can block the airway.
It’s key to know what causes angioedema and how it relates to chronic hives. By treating the causes and using the right medicine, people can feel better. This improves their life quality a lot.
| Condition | Prevalence | Causes | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Hives | Affects up to 50% of individuals for over 6 weeks | Can be idiopathic (unknown cause) or triggered by factors like allergies, stress, or underlying medical conditions | Persistent skin rashes, itching, and swelling |
| Angioedema | Over 50% of patients may have their first swelling episode before age 12 | Triggered by medications, foods, and other factors that cause the release of chemicals like histamine | Swelling of the deeper skin layers, often around the eyes, cheeks, or lips |
“Understanding the connection between chronic hives and angioedema is important, as the presence of both conditions may require specialized treatment approaches.”
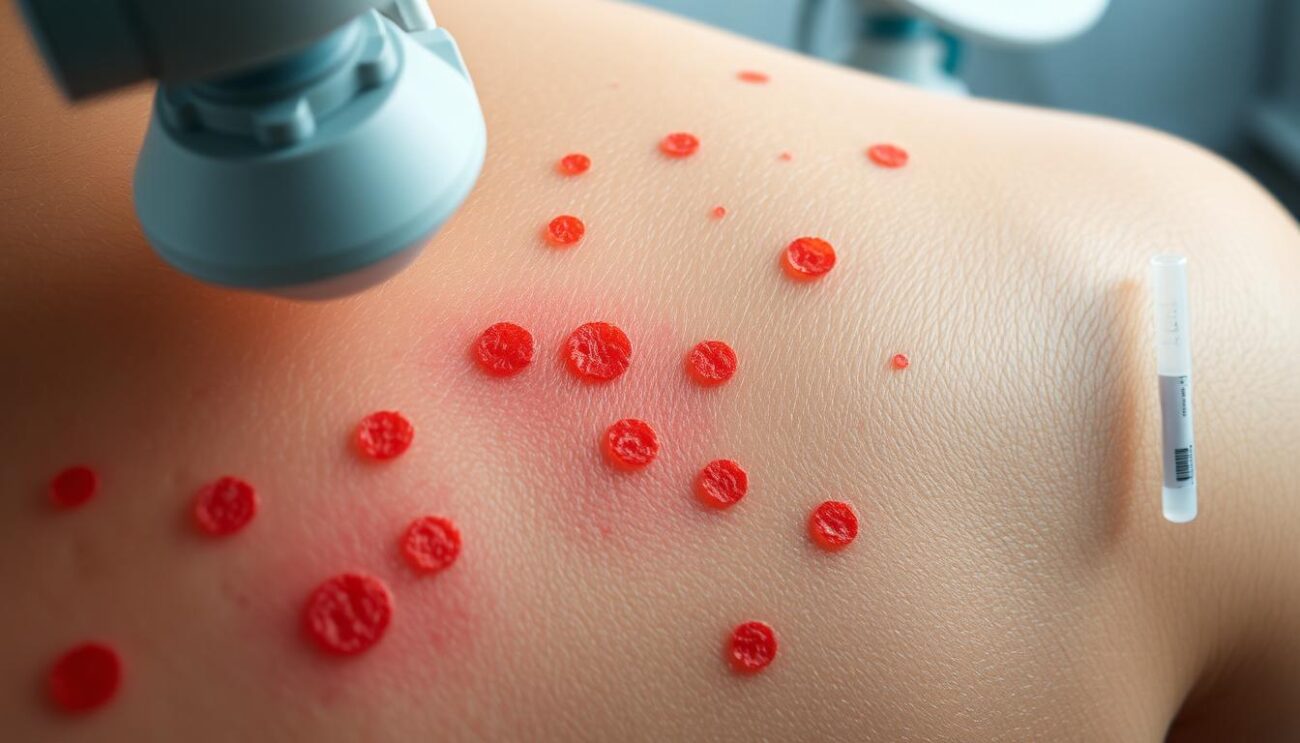
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing chronic hives starts with a detailed medical history and physical exam. A healthcare provider, like an allergist or dermatologist, will look into your symptoms. They want to know how long you’ve had hives, how often, and what they look like. They also ask about any possible triggers or health issues.
Medical History Evaluation
Understanding your medical history is key to diagnosing chronic hives. Your healthcare provider will ask several questions:
- When did your hives start?
- How often and how severe are they?
- Have you noticed any triggers, like certain foods or medicines?
- Do you have any other health conditions or allergies?
This info helps the provider find the root cause of your hives. They might also suggest diagnostic tests, like blood work or allergy tests, to learn more.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood Tests | To check for underlying medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases, that may be contributing to the chronic hives. |
| Allergy Testing | To identify any food or environmental allergies that may be triggering the hives. |
| Skin Tests | To assess the patient’s reaction to potential triggers, such as cold, heat, or pressure. |
By looking at your medical history and doing tests, healthcare providers can find the cause of your hives. Then, they can create a treatment plan just for you.
Management and Treatment Options
Managing chronic hives involves a mix of treatments. The main goal is to ease the itch, swelling, and discomfort. This helps those with chronic spontaneous urticaria.
Antihistamines: The First Line of Defense
Antihistamines like cetirizine or loratadine are often the first choice. They block histamine, which causes hives and itching. A 2007 study by Godse KV showed fexofenadine and levocetirizine work equally well.
Steroids and Immunosuppressants: Managing Severe Cases
For severe cases, doctors might use steroids or immunosuppressants. These can control inflammation but come with risks. Patients need close monitoring.
Emerging Treatments: Omalizumab and Biologics
New treatments like omalizumab have been approved for chronic idiopathic urticaria. It targets IgE, key in allergies. Studies show omalizumab improves symptoms in a few months.
Other biologics, like Dupilumab, are also being studied. They aim to reduce inflammation. These options offer targeted treatments for severe cases.
Managing chronic hives requires teamwork between patients and doctors. Treatment plans are customized based on individual needs and condition severity.
Conclusion
Chronic hives, or persistent urticaria, is a complex skin condition. It can greatly affect a person’s quality of life. Knowing the chronic hives causes, like environmental factors and autoimmune disorders, is key for managing it. Working with healthcare providers is crucial for finding the right treatment.
Persistent urticaria can come from many sources, including food allergies and infections. A detailed medical history and tests are needed to find the cause. This helps in creating a treatment plan that can bring relief from the symptoms.
Research is ongoing to better understand chronic hives causes and how to manage them. This research helps doctors find more effective treatments. It gives hope to those with chronic hives, helping them control their symptoms and improve their well-being.