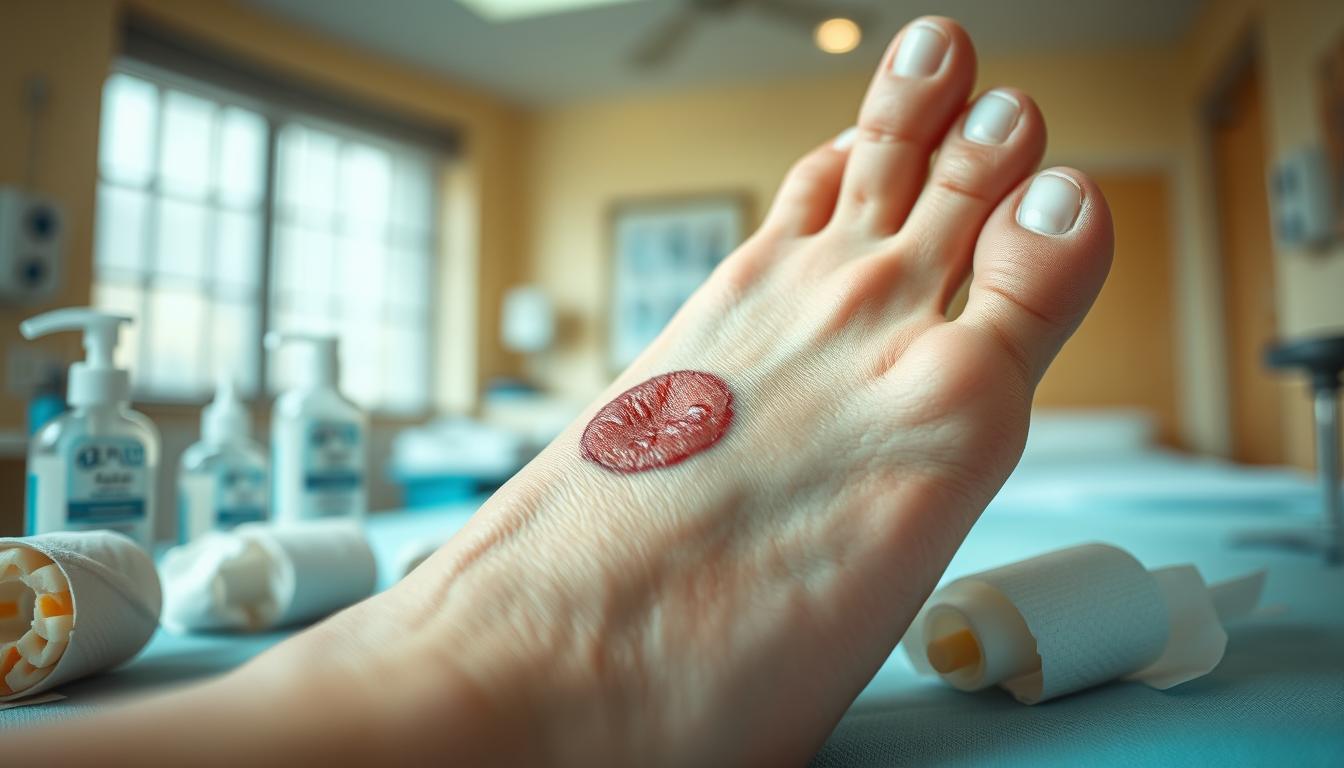
Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious problem for people with diabetes. They can lead to infection, hospital stays, and even amputation if not treated. But, there are effective ways to prevent these bad outcomes. As a professional copywriter, I’m here to share the latest in treating diabetic foot ulcers and challenge what you might think.
Dealing with diabetic foot ulcers needs a mix of strategies. These include stopping infections, taking pressure off, helping wounds heal, and fixing the root causes. Healthcare teams use advanced products and new ways to reduce pressure to help patients with diabetes. But, do these methods really work? And how can patients and their caregivers get the best results? Let’s find out.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to infection, hospitalization, and amputation if left untreated.
- Effective treatment options focus on preventing infection, offloading pressure, debridement, and promoting wound healing.
- A multidisciplinary approach involving podiatrists, vascular specialists, and other healthcare providers is crucial for managing diabetic foot ulcers.
- Key treatment strategies include glycemic control, revascularization, advanced wound care products, and patient education on proper foot care.
- Innovative offloading techniques and infection control measures are essential for reducing the risk of complications and promoting ulcer healing.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Definition and Prevalence
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore on a person with diabetes’s foot. It’s a big problem, as about 15% of people with diabetes get a foot ulcer. These ulcers are a top reason for hospital stays and amputations, making them very serious for those with diabetes.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several things can lead to diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetic neuropathy makes feet less sensitive, and peripheral arterial disease hinders blood flow and healing. Other risks include foot deformities, poor foot care, and high blood sugar. Knowing these risks helps prevent and treat diabetic foot ulcers.
“Foot ulceration is associated with a 5-year survival rate of 50 to 60% after presentation.”
Recent studies show the yearly rate of diabetic foot ulceration is about 2.2%. The lifetime risk of getting a foot ulcer can be as high as 34%. Also, up to 40% of patients see a foot ulcer again within a year. These numbers highlight the need for better management and prevention to tackle this major health issue.
Comprehensive Assessment and Diagnosis
Getting a proper diagnosis for diabetic foot ulcers is key to the right treatment. This involves a detailed physical examination, imaging, and laboratory tests. These steps help find the cause and any complications.
Physical Examination Techniques
The first step is checking sensation, circulation, and foot deformities. A monofilament test can spot sensory loss due to diabetic neuropathy. Checking vascular assessment is also important, using pulses and Doppler ultrasound.
Looking for foot deformities, like Charcot foot, is also key.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
Imaging for osteomyelitis uses X-rays, MRI, and nuclear scans. These help find bone and soft tissue issues. Laboratory tests for infection include cultures and inflammatory markers. These tests are vital for diagnosis.
Probe-to-bone testing helps check for osteomyelitis.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Monofilament testing | Assess diabetic neuropathy |
| Doppler ultrasound | Evaluate peripheral arterial disease |
| X-rays, MRI, nuclear scans | Imaging for osteomyelitis |
| Wound cultures, inflammatory markers | Laboratory tests for infection |
| Probe-to-bone test | Assess for underlying osteomyelitis |
Using a thorough diabetic foot ulcer physical examination and the right tests helps doctors find the cause. This way, they can create a good treatment plan for diabetic foot ulcers.
Essential Wound Care Principles
Effective wound care is key for healing and avoiding problems in diabetic foot ulcers. It involves several important steps. These include debridement, choosing the right dressings, and using topical treatments.
Debridement Methods
Debridement is the first step in treating diabetic foot ulcers. It removes dead, infected, or dying tissue. There are different ways to do this, like:
- Mechanical debridement, such as scrubbing or wound irrigation, to physically remove devitalized tissue
- Enzymatic debridement, using topical agents that break down necrotic tissue
- Autolytic debridement, which uses the body’s natural healing to break down dead tissue
Dressings and Topical Agents
Choosing the right dressings and topical agents is vital. They help keep the wound moist and manage fluid. Advanced dressings, like hydrogels and foams, create a good healing environment. Topical therapies, including growth factors, can also help.
By following these wound care principles, healthcare professionals can manage diabetic foot ulcers well. This promotes healing and lowers the chance of complications.
diabetic foot ulcer treatment
Managing diabetic foot ulcers needs a mix of steps. These include reducing pressure and controlling infections. Offloading the area is key to healing and avoiding more problems.
Offloading and Pressure Redistribution
Using total contact casts, removable walkers, and special shoes helps. These tools spread out the weight and help the ulcer heal. They are made to lessen the chance of more ulcers.
Infection Control and Antimicrobial Therapy
Not fighting infections can cause big problems. So, treating any infections is very important. Doctors use antibiotics based on tests to clean and dress the wound. This whole plan is key to treating diabetic foot ulcers well.
| Key Aspects of Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment | Importance |
|---|---|
| Diabetic foot ulcer offloading | Reduces pressure on the affected area, promoting healing |
| Pressure relief devices | Redistribute weight and minimize the risk of further ulceration |
| Diabetic foot ulcer infection management | Addresses co-existing infections to prevent serious complications |
| Antibiotic therapy | Tailored to wound cultures and sensitivity testing for effective treatment |
Healthcare teams use offloading and infection control together. This way, they can better treat diabetic foot ulcers and help patients get better.
Revascularization and Surgical Interventions
For diabetic foot ulcers with peripheral arterial disease, doctors might use angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery. These methods help improve blood flow and aid in healing. They aim to prevent amputation and support diabetic foot ulcer revascularization.
In some cases, surgical treatment options are needed. They help offload pressure, improve wound healing, and stop amputation. This can include fixing foot deformities or removing infected bone.
| Procedure | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty | Minimally invasive procedure that widens narrowed or blocked arteries | Improves blood flow, promotes wound healing, and reduces amputation risk |
| Stenting | Placement of a small mesh tube to hold the artery open and improve blood flow | Maintains artery patency, enhances blood supply, and supports tissue repair |
| Bypass Surgery | Surgical procedure that reroutes blood flow around a blocked or diseased artery | Restores adequate blood supply, facilitates wound healing, and prevents amputation |
Choosing the right diabetic foot ulcer revascularization or surgery depends on several factors. These include the disease’s extent and location, the patient’s health, and the procedure’s benefits and risks. A team of vascular specialists, podiatrists, and wound care experts is key to the best outcomes and avoiding limb loss.
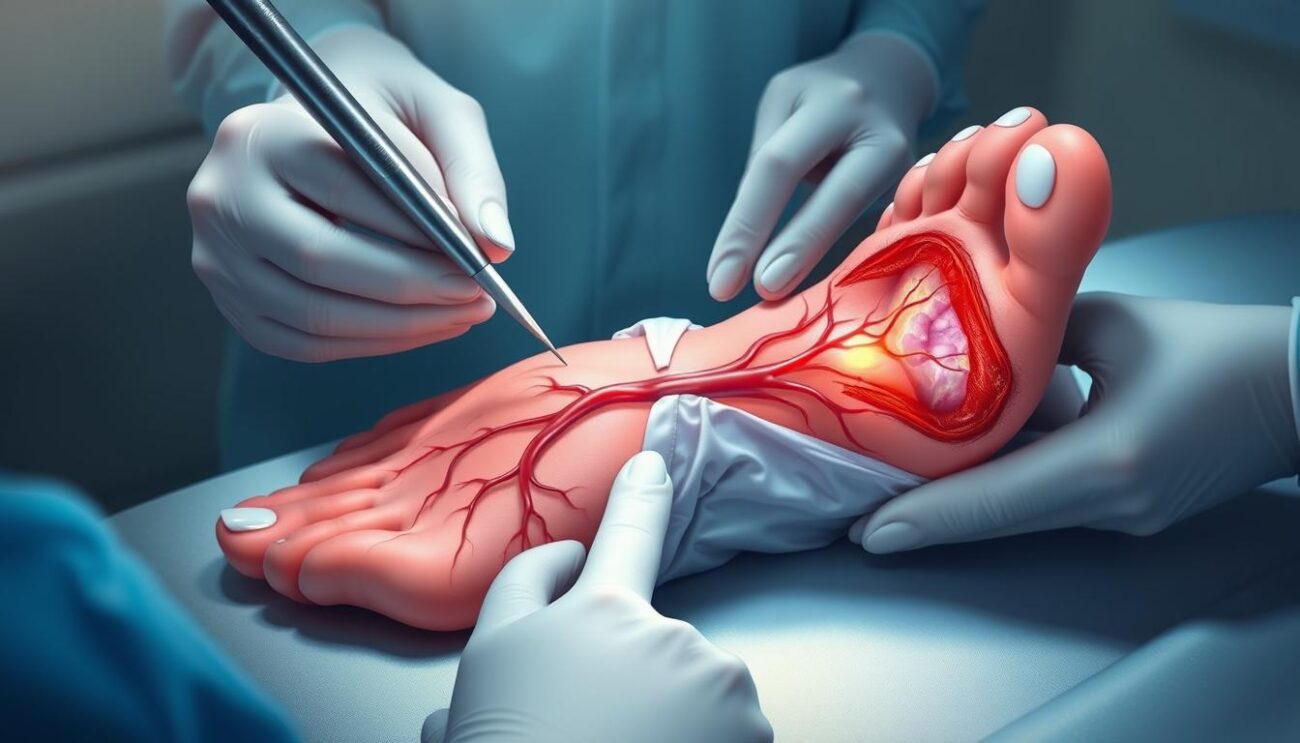
Adjunctive and Emerging Therapies
Several advanced diabetic foot ulcer treatments are being explored. These include growth factor therapy and skin substitutes. They aim to help wounds heal faster and better.
These new treatments show promise. But, more research is needed to make them work better and be more affordable. The cost of care for diabetic foot ulcers is high, especially when patients need to stay in the hospital.
Growth Factors and Skin Substitutes
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is a growth factor therapy being studied. It helps wounds heal by promoting cell growth and blood vessel formation. Skin substitutes offer a framework for healing by using bioengineered tissues.
These treatments are promising. Yet, they need more work to be widely used and affordable. The high cost and limited evidence are major hurdles.
| Therapy | Effectiveness | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) | Stimulates cellular proliferation and angiogenesis | Further research needed to optimize clinical application and cost-effectiveness |
| Skin substitutes | Provides a scaffold for novel wound healing modalities | High unit cost and lack of robust evidence are limitations |
“Adjuvant therapies are more likely to be cost-effective in patients identified as ‘hard to heal.'”
Glycemic Control and Comorbidity Management
Keeping blood sugar levels in check is key to treating diabetic foot ulcers. High blood sugar can slow down healing, raise infection risk, and lead to other diabetes problems. It’s also important to manage comorbidities like high blood pressure, bad cholesterol, and kidney disease. This helps wounds heal better and lowers the chance of losing a limb.
The 7th edition of the Diabetes Atlas from the International Diabetes Federation highlights the big problem of diabetic foot ulcers worldwide. Issues like nerve damage and poor blood flow make foot ulcers come back. Kidney failure also raises the risk of foot problems or amputation in people with diabetes.
| Comorbidity | Impact on Diabetic Foot Ulcers |
|---|---|
| Peripheral Neuropathy | Increases risk of plantar foot ulcer recurrence |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease | Impairs wound healing and increases amputation risk |
| Renal Failure | Associated with higher risk of foot ulcers and amputations |
To help diabetic foot ulcers heal, a full plan that focuses on glycemic control and comorbidity management is needed. This approach can lower infection risk, speed up healing, and stop amputations.
“Approximately 40% of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes mellitus lead to diabetes-related foot infections, which contributed to over 130,000 lower-extremity amputations in the United States in 2016.”
Prevention and Patient Education
Stopping diabetic foot ulcers is key, as they can lead to serious issues like amputation. Regular foot checks, clean feet, and the right shoes are vital. Teaching patients about daily foot checks and lifestyle changes can lower the risk of these ulcers.
Foot Care and Lifestyle Modifications
About 5 percent of people with diabetes face amputation of a toe or foot. Annual foot exams are crucial, starting five years after diagnosis for type 1 diabetes and at diagnosis for type 2. Foot ulcers affect 15% to 25% of people with diabetes, leading to 25% to 90% of amputations.
Good prevention includes:
- Checking feet daily for cuts, blisters, or infections
- Keeping feet clean and dry
- Wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes
- Quitting smoking to improve circulation and healing
- Staying at a healthy weight to reduce foot pressure
By teaching patients about diabetic foot ulcer prevention and promoting lifestyle changes, healthcare providers can lower the risk of these serious problems. This improves foot care education for those with diabetes.
| Preventive Measure | Impact |
|---|---|
| Annual foot exams | Reduce amputation risk by early detection of issues |
| Daily foot inspections | Identify problems early before they worsen |
| Proper foot hygiene | Maintain skin integrity and prevent infections |
| Appropriate footwear | Protect feet and reduce pressure-related injuries |
| Lifestyle changes | Improve overall health and wound healing |
By using these diabetic foot ulcer prevention methods and giving thorough foot care education, healthcare providers can help patients manage their risk factor modification. This reduces the chance of these serious complications.
“Prevention is better than cure. Educating patients on proper foot care and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers and the need for costly and life-altering amputations.”
Multidisciplinary Collaborative Care
Managing diabetic foot ulcers needs a team effort. Healthcare experts from different fields work together. They focus on wound care, offloading, revascularization, and infection control.
This teamwork helps create a treatment plan that’s all about the patient. It boosts the chances of healing the wound and saving the limb.
The team includes podiatrists, vascular surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and wound care nurses. They work together to save the limb. They tackle the medical, surgical, and lifestyle issues that cause these ulcers.
- Podiatrists check the foot, do debridement, and use offloading to ease pressure.
- Vascular surgeons handle vascular disease, doing procedures to help blood flow.
- Infectious disease specialists find and treat infections, making sure antibiotics are right.
- Wound care nurses use advanced techniques like dressings and topical agents.
This team effort leads to better care for patients. It cuts down amputation rates and improves life quality for those with diabetic foot ulcers.
“Establishing integrated interdisciplinary teams, critical pathways, and diabetic foot units leads to enhanced care coordination, decreased incidence of major amputations, and improved outcomes for individuals with diabetic foot ulcers.”
Conclusion
Diabetic foot ulcers are a big problem in healthcare. They affect 19% to 34% of people with diabetes. Sadly, 50% to 70% of those with these ulcers die within 5 years, and 5% may lose a limb.
But, with the right treatment, doctors can help these patients heal. This approach includes many steps to prevent serious problems.
Effective treatment for diabetic foot ulcers includes several key steps. These include taking pressure off the foot, controlling infections, improving blood flow, and using advanced wound care. Special devices can reduce pressure by up to 87%.
For ulcers that don’t heal, doctors might use special treatments. These include products from placental tissue, certain dressings, and oxygen therapy in a pressurized chamber.
Working together is crucial in treating diabetic foot ulcers. Doctors from different fields, like podiatry and vascular surgery, team up. This ensures each patient gets the best care tailored to their needs.
This team effort, along with educating patients and keeping a close eye on them, is key. It helps achieve the best results and lessens the impact of these ulcers.