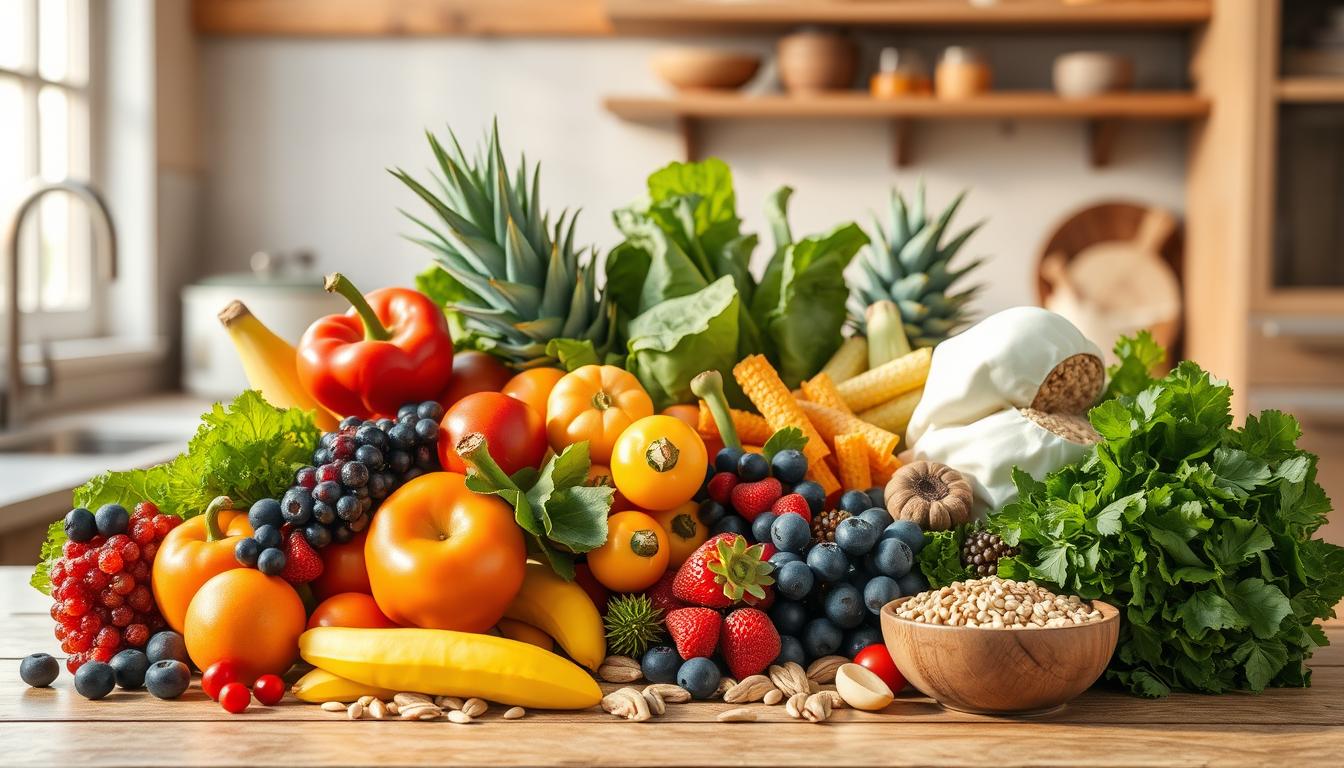
Could a simple change in what you eat help manage diabetes and boost your health? The answer might just surprise you. Studies show that diet plays a huge role in controlling diabetes. So, creating a healthy eating plan is key for those with this chronic condition.
Key Takeaways
- A diabetes-friendly diet is rich in nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Portion control and carbohydrate counting are essential for managing blood sugar levels.
- Incorporating healthy fats and limiting saturated and trans fats can improve heart health.
- Avoiding so-called “diabetic foods” and focusing on whole, unprocessed foods is key.
- Regular physical activity plays a vital role in managing diabetes and reducing complications.
Understanding the Importance of Diet in Diabetes Management
For those with diabetes or prediabetes, a healthy diet is key. It helps control blood sugar, manage weight, and lower heart disease risk. A diabetes diet keeps blood sugar safe by choosing nutritious foods and tracking what you eat.
Why Developing a Healthy Eating Plan is Crucial
Weight loss can also help manage diabetes. The American Diabetes Association suggests a diet rich in nutrients but low in fat and calories. Focus on fruits, veggies, whole grains, legumes, and low-fat dairy. This diet not only controls blood sugar but also lowers heart disease and cancer risks.
How Diet Affects Blood Sugar Levels and Complications
High blood sugar can cause serious problems like nerve, kidney, and heart damage. Eating well keeps blood sugar safe. It also helps with weight loss, offering more health benefits.
| Nutrient | Impact on Diabetes |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels, and individuals may need to adjust their insulin doses accordingly. |
| Fiber | Fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, can help slow the absorption of carbohydrates and stabilize blood sugar levels. |
| Healthy Fats | Incorporating healthy fats, like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, is recommended to lower cholesterol levels and support heart health. |
“Following a healthy-eating plan not only helps individuals keep their blood sugar levels under control but also presents additional benefits like lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers while reducing the risk of low bone mass in the future.”
Recommended Foods for a Diabetic Diet
Creating a diabetes-friendly diet is key to managing blood sugar and avoiding complications. Focus on healthy carbohydrates and fiber-rich foods. These help with digestion and keep blood sugar stable.
Healthy Carbohydrates: Fruits, Vegetables, and Whole Grains
Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are great for diabetics. They are full of nutrients and don’t raise blood sugar as much as processed carbs. Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables adds vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to your diet.
Fiber-Rich Foods: Legumes, Nuts, and Whole Grains
Fiber-rich foods like legumes, nuts, and whole grains are vital for diabetes control. They help manage blood sugar and offer extra health benefits. These include feeling full and supporting digestion.
| Healthy Carbohydrate Sources | Fiber-Rich Foods |
|---|---|
|
|
Adding these healthy carbohydrates and fiber-rich foods to your diet helps manage diabetes. It also supports your overall health.
Heart-Healthy Choices
Managing diabetes means focusing on a heart-healthy diet. It’s important to add fatty fish and good fats to your meals. Eating salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines at least twice a week gives you omega-3 fatty acids. These may help prevent heart disease.
Also, adding foods with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats is good. Think avocados, nuts, and plant-based oils. They can lower cholesterol and reduce heart disease risk.
Incorporating Fatty Fish and Good Fats
Heart disease is a big killer in the U.S., especially for people with diabetes over 65. Eating at least five servings of nuts a week can lower heart disease risk. A heart-healthy diet with fatty fish and good fats is key for those with diabetes.
| Nutrient | Benefits for Heart Health |
|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Help prevent heart disease and reduce inflammation |
| Monounsaturated Fats | Lower cholesterol and improve insulin sensitivity |
| Polyunsaturated Fats | Reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke |
By choosing these heart-healthy foods, you can support your heart health. This helps manage diabetes better.
Foods to Avoid or Limit
A diabetes-friendly diet focuses on whole foods. But, it’s also key to limit certain foods. These include high-fat dairy, animal proteins, and processed snacks. They are often high in saturated fats and trans fats.
Too much cholesterol and sodium can harm health. It can make diabetes issues worse.
Saturated and Trans Fats
Saturated fats are in full-fat dairy, fatty meats, and tropical oils. They can raise cholesterol levels and increase heart disease risk. Trans fats, found in fried foods and baked goods, can cause inflammation and insulin resistance.
It’s important to limit these unhealthy fats. This helps manage diabetes and keeps the heart healthy.
Cholesterol and Sodium
High cholesterol and sodium levels are risky for diabetics. Foods high in cholesterol, like high-fat dairy, can lead to plaque buildup. This increases heart disease risk.
Too much sodium, found in processed foods, can cause high blood pressure. This strains the heart.
By avoiding or limiting these foods, diabetics can manage their condition better. They can also reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health.
Managing Diabetes Through Diet: Meal Planning Strategies
Effective meal planning is key for managing diabetes through diet. Two main methods help control blood sugar: the plate method and counting carbs. Understanding the glycemic index of foods is also important.
The Plate Method: Balancing Portions
The plate method is simple and effective for portion control. It suggests filling half the plate with non-starchy veggies, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with carbs. This balance helps manage blood sugar and promotes healthy eating.
Carbohydrate Counting and Glycemic Index
Carbohydrate counting involves estimating carbs in a meal and matching it with insulin. The glycemic index of foods also plays a big role. It shows how quickly foods raise blood sugar. Choosing low-glycemic foods helps keep blood sugar stable.
Using these meal planning strategies, people with diabetes can manage their condition. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet supports their health and well-being.
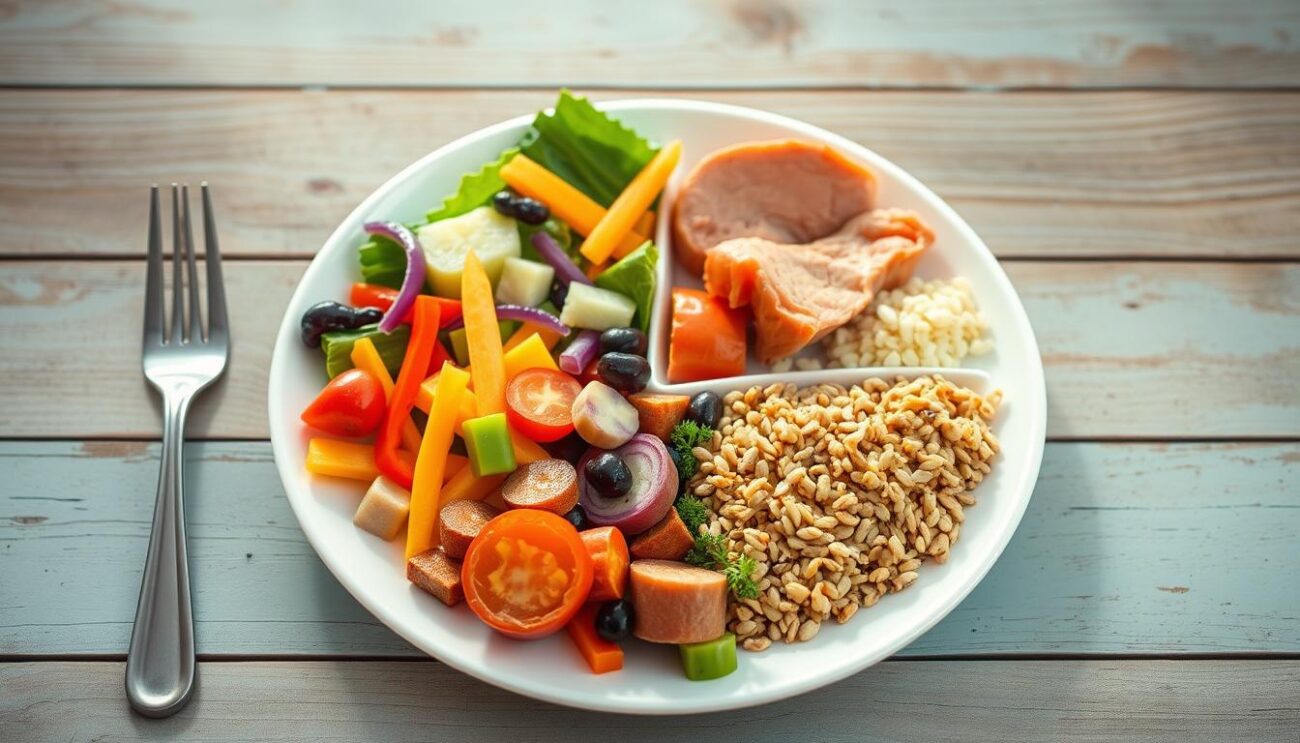

“Effective meal planning is a key strategy for managing diabetes through diet.”
Making Healthier Food Choices
Managing diabetes through diet means making better food choices. Focus on healthy carbohydrates and proteins. Also, cut down on sodium and added sugars. These changes help control blood sugar, improve health, and lower diabetes risks.
Choosing Healthier Carbohydrates and Proteins
Choose healthy carbohydrates like fruits, veggies, and whole grains. They’re full of nutrients and fiber. Stay away from refined carbs like white bread and sugary snacks, as they raise blood sugar.
For proteins, pick lean ones like fish, poultry, legumes, and nuts. They help manage blood sugar well.
Reducing Sodium and Added Sugars
It’s important to limit sodium intake for diabetes management. High sodium can lead to high blood pressure and heart problems. Try to stay under 2,300 mg of sodium daily.
Also, cut down on added sugars from sweet drinks and processed foods. This helps keep blood sugar in check and prevents weight gain.
“Diverse carbohydrate intake can be appropriate, with both very high and low intakes associated with premature mortality.”
Talking to a healthcare team, like a registered dietitian, is a good idea. They can help create a meal plan that fits your health goals and likes. Making these food choices can help manage diabetes better and improve your health.
Remember, a balanced diet is key for diabetes management. Eating a variety of healthy foods, reducing sodium and added sugars, and staying active are all important. They help manage diabetes and improve your health.
The Role of Physical Activity
Alongside a healthy diet, physical activity is key in managing diabetes. It helps the body use glucose better, leading to better blood sugar control. It also lowers the risk of heart disease and other diabetes-related problems.
Recent stats show that 34.3% of Americans with diabetes are not active. They do less than 10 minutes a week of moderate or vigorous activity. But, 23.8% of them meet the 150-minute weekly activity guideline.
To help manage your diabetes and stay healthy, aim for 150 minutes of moderate activity each week. Activities like brisk walking are good. Doing more than 12 METs of exercise can lower your diabetes risk by 54% compared to less than 6 METs.
| Insufficient Physical Activity Levels | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Worldwide | 27.5% |
| Women in Latin America and the Caribbean | 43.7% |
| Women in South Asia | 43.0% |
| Women in High-income Western Countries | 42.3% |
| Men in Oceania | 12.3% |
Physical activity is crucial for diabetes management. It boosts insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscles. It also reduces heart disease risk. By adding physical activity to your daily life, you can manage your diabetes better and improve your health.
Debunking Myths: No Such Thing as “Diabetic Foods”
There’s a big myth about diabetic foods. Many think special “diabetic” products are needed. But, this is not true. These diabetic foods don’t have special benefits. They are not different from a healthy diet that anyone can do, including those with diabetes management.
Many diabetic foods can still raise blood sugar levels. They have as much fat and calories as regular foods. Instead, focus on eating a variety of healthy, whole foods. This is key for a good diabetes management plan.
- Diabetic foods do not provide any special benefits for managing blood sugar levels.
- These specialized products can still impact blood sugar and contain similar amounts of fat and calories as regular items.
- A healthy, balanced diet with a focus on whole, unprocessed foods is the best approach for effective diabetes management.
By clearing up the myth of “diabetic foods,” people with diabetes can make better choices. They can create a lasting healthy eating plan that fits their needs. The main thing is to choose foods that are full of nutrients and support health.
Getting Nutrients from Food, Not Supplements
Managing diabetes through diet is best done by eating whole, nutrient-rich foods. There’s no solid proof that vitamin or mineral supplements help people with diabetes. Some supplements can even harm by interacting with diabetes meds or making health problems worse.
Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is key. This way, you get all the nutrients you need without supplements. Whole foods have many good compounds that work together to keep you healthy.
The American Diabetes Association says supplements don’t help unless you’re lacking a nutrient. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) suggest getting half your calories from carbs. Choose high-fiber carbs, lean proteins, and healthy fats to keep blood sugar stable.
Always talk to your doctor before starting any supplement. Some can change blood sugar levels, leading to low or high blood sugar. Choose supplements with the USP (United States Pharmacopeia) symbol for quality and purity.
| Nutrient Deficiencies | Recommended Dietary Sources |
|---|---|
| Iron, Vitamins D and B12, Magnesium, Calcium | Leafy greens, fatty fish, eggs, legumes, nuts and seeds |
In conclusion, focus on getting nutrients from whole foods, not supplements, when managing diabetes through diet. A balanced diet meets your nutritional needs and supports your health. This approach avoids the risks and interactions of supplements.
“There’s no single ‘magic’ diet for diabetes, as everyone’s body responds differently to different types of foods and diets.” – American Diabetes Association
Conclusion
Starting a healthy, diabetes-friendly diet is key to managing diabetes. Eating nutrient-rich, whole foods and controlling portions helps. It also keeps your blood sugar levels in a healthy range and aids in weight management.
Using methods like the plate method and carbohydrate counting is helpful. These strategies reduce the risk of diabetes complications. It’s important to remember that everyone’s diet needs are different. So, work with your healthcare team to create a diet plan that fits you.
With the right diet, you can manage your diabetes and support your long-term health. This approach lets you take an active role in your health.
For those with diabetes, a balanced healthy eating plan is crucial. Eating a variety of nutritious foods and controlling carbs is key. Making heart-healthy choices also helps manage blood sugar levels and lowers complication risks.
Getting regular check-ups and personalized advice from healthcare professionals is vital. They can guide you in making lifestyle changes. This helps you take control of your diabetes and look forward to a healthier future.
The journey to better diabetes management is continuous. It’s a chance to try new recipes and find what works for you. With determination and a proactive mindset, you can manage your diabetes effectively. This supports your overall health and well-being for the long term.