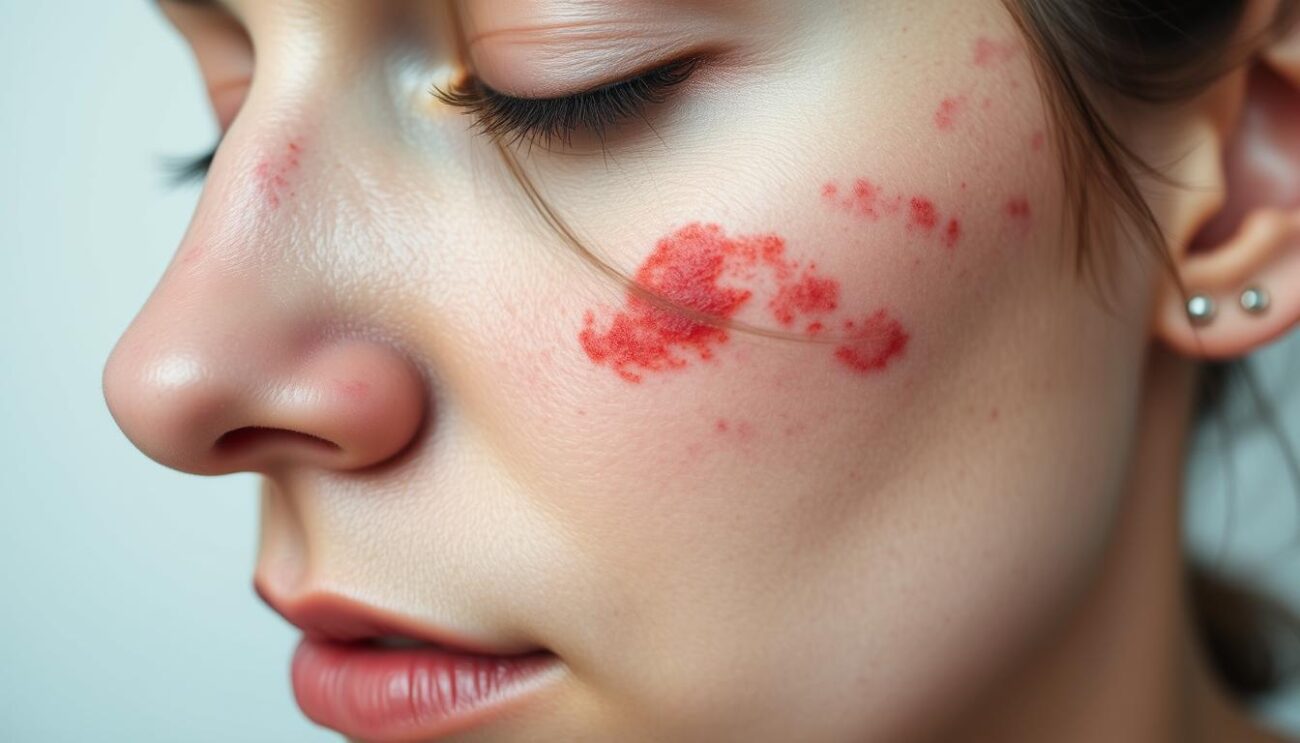
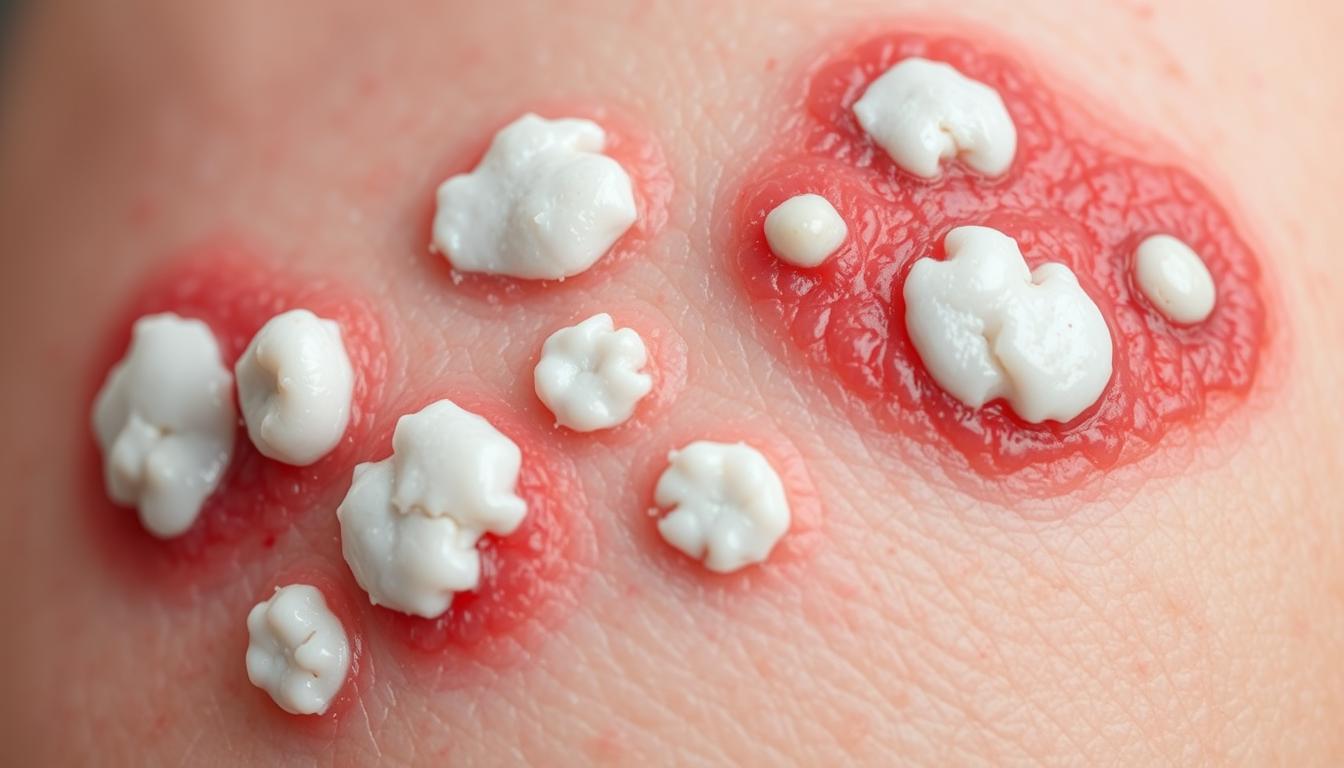
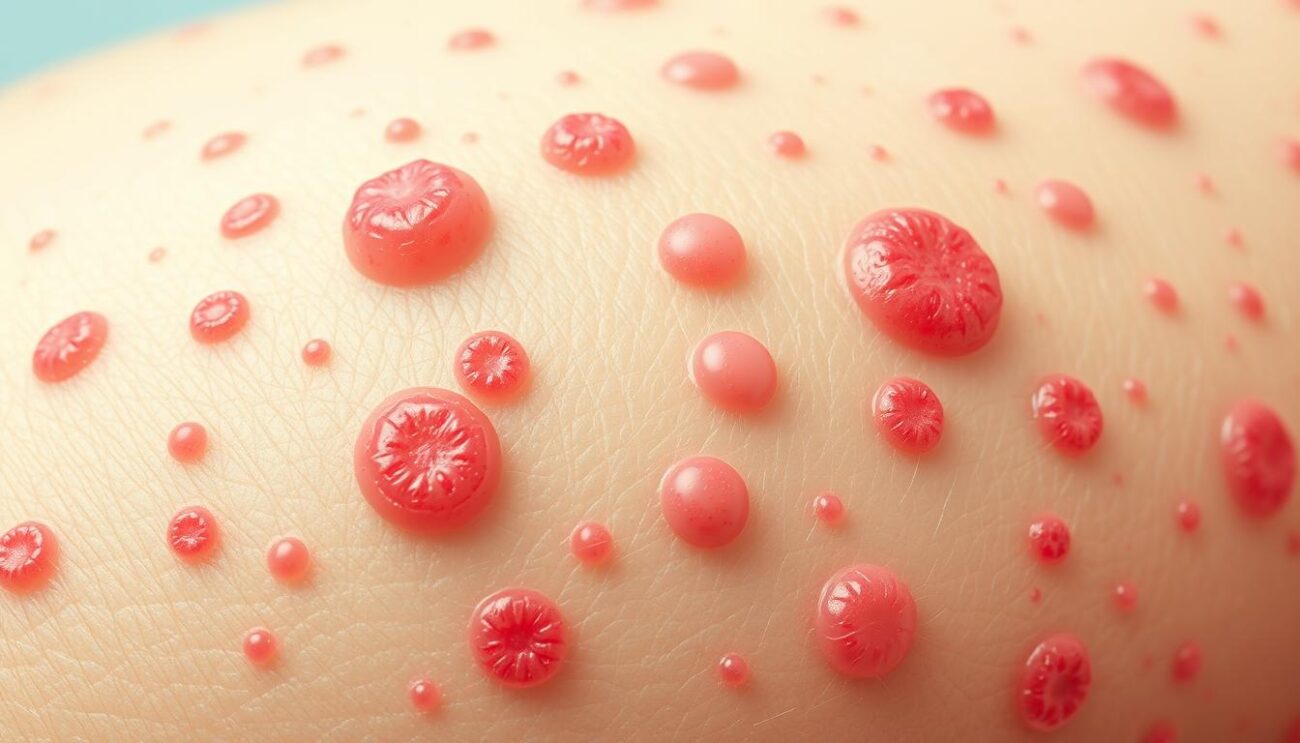
Ever wondered what’s happening under your skin? Pustular psoriasis is a form of psoriasis that can surprise you. It causes painful blisters filled with pus, leading to a red, scaly rash. This can be very painful and upsetting.
So, what is pustular psoriasis, and how can you deal with it? Let’s explore the causes, symptoms, and ways to treat it.
Key Takeaways
- Pustular psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that causes pus-filled blisters and inflamed skin.
- It can appear on various parts of the body, including the palms, soles, and even the fingertips.
- Triggers for pustular psoriasis can include stress, infections, medications, and hormonal changes.
- Treatment options include topical therapies, phototherapy, oral medications, and biologic therapies.
- Proper skin care, stress management, and seeking support can help manage the condition.
What is Pustular Psoriasis?
Pustular psoriasis is a rare and severe form of psoriasis. It causes inflamed, pus-filled blisters or pustules on the body. These often appear on the hands and feet.
This condition is caused by an overactive immune system. It mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to the painful pustules.
Types of Pustular Psoriasis
There are several types of pustular psoriasis. Each has its own symptoms and severity:
- Generalized Pustular Psoriasis (von Zumbusch psoriasis): This is the most severe form. It causes widespread, itchy pustules. Symptoms include fever, fatigue, and weight loss.
- Palmoplantar Pustulosis: This type affects the palms and soles. It causes painful, blistered rashes.
- Acrodermatitis Continua of Hallopeau: This rare form causes painful pustules on fingers and toes. It can damage nails and joints over time.
- Localized Pustular Psoriasis: This type is limited to specific areas. It can affect the face, genitals, or limbs.
All forms of pustular psoriasis are serious and potentially life-threatening. They need prompt medical attention and proper treatment.
Symptoms of Pustular Psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis shows up as white or yellow bumps filled with pus. These bumps are surrounded by red, inflamed skin. They often appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Sometimes, they can also show up on fingers, toes, or other areas.
Physical Manifestations
The main signs of pustular psoriasis are:
- Inflamed pustules – White or yellow, pus-filled bumps surrounded by red, scaly skin
- Red scaly rash – Patches of inflamed, reddened skin
- Palmoplantar pustulosis – Painful pustules on the palms and soles
- Von Zumbusch psoriasis – Widespread, fiery-red skin with many large pustules
- Generalized pustular psoriasis – Sudden, widespread eruption of painful pustules
Accompanying Symptoms
Pustular psoriasis also brings other symptoms, like:
- Severe itching – The inflamed, pustular skin can be extremely itchy and uncomfortable.
- Fever and chills – Generalized pustular psoriasis in particular can cause fever, chills, and other flu-like symptoms.
- Muscle weakness – The inflammation and systemic effects of the condition may lead to muscle weakness and fatigue.
These symptoms can really affect a person’s life. They might need to see a doctor right away, especially if they have generalized pustular psoriasis.
Causes and Triggers
Pustular psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. This means the body’s immune system attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to inflamed pustules. The exact cause is still a mystery, but genetics and triggers play a role.
Autoimmune Response
In pustular psoriasis, the immune system causes inflammation. This leads to fast skin cell production and pus-filled lesions. Genes like IL36RN and AP1S3 might make some people more likely to get it.
Potential Triggers
- Certain medications, including antimicrobials and systemic steroids
- Sudden changes in medication
- Infections
- Stress
- Pregnancy and hormonal changes
- Exposure to too much ultraviolet light
Knowing and avoiding these triggers can help manage symptoms. It can also prevent flare-ups.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Men and women affected equally | Yes |
| Average age of onset | Around 50 years old |
| Rare in children aged 2-10 | Yes |
| More common in boys than girls (when it occurs in children) | Yes |
| Alcohol consumption increases susceptibility in men | Yes |
| Smoking increases severity of flare-ups | Yes |
| Excess weight increases severity | Yes |
Understanding pustular psoriasis and its triggers helps manage it. Working with healthcare providers is key. This way, people can live better despite the condition.
Diagnosing Pustular Psoriasis
Diagnosing pustular psoriasis starts with a detailed medical history and physical examination by a dermatologist. They look for pus-filled blisters and inflammation on the skin. Sometimes, a skin biopsy is taken for a closer look under a microscope.
Blood tests might also be done to check for infections or other factors. This helps find the cause of the condition.
The doctor also checks to see if it’s not another skin condition like acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) or impetigo. This step is crucial for a correct diagnosis and the right treatment.
| Diagnostic Approach | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Gather information about the patient’s symptoms, onset, and potential triggers |
| Physical Examination | Visually inspect the skin for the characteristic pustular lesions |
| Skin Biopsy | Analyze a small sample of affected skin under a microscope for definitive diagnosis |
| Blood Tests | Identify any underlying infections or other contributing factors |
| Ruling Out Other Conditions | Differentiate pustular psoriasis from similar-looking skin conditions |
By using these methods, doctors can accurately diagnose pustular psoriasis. They then create a treatment plan to manage the condition effectively.
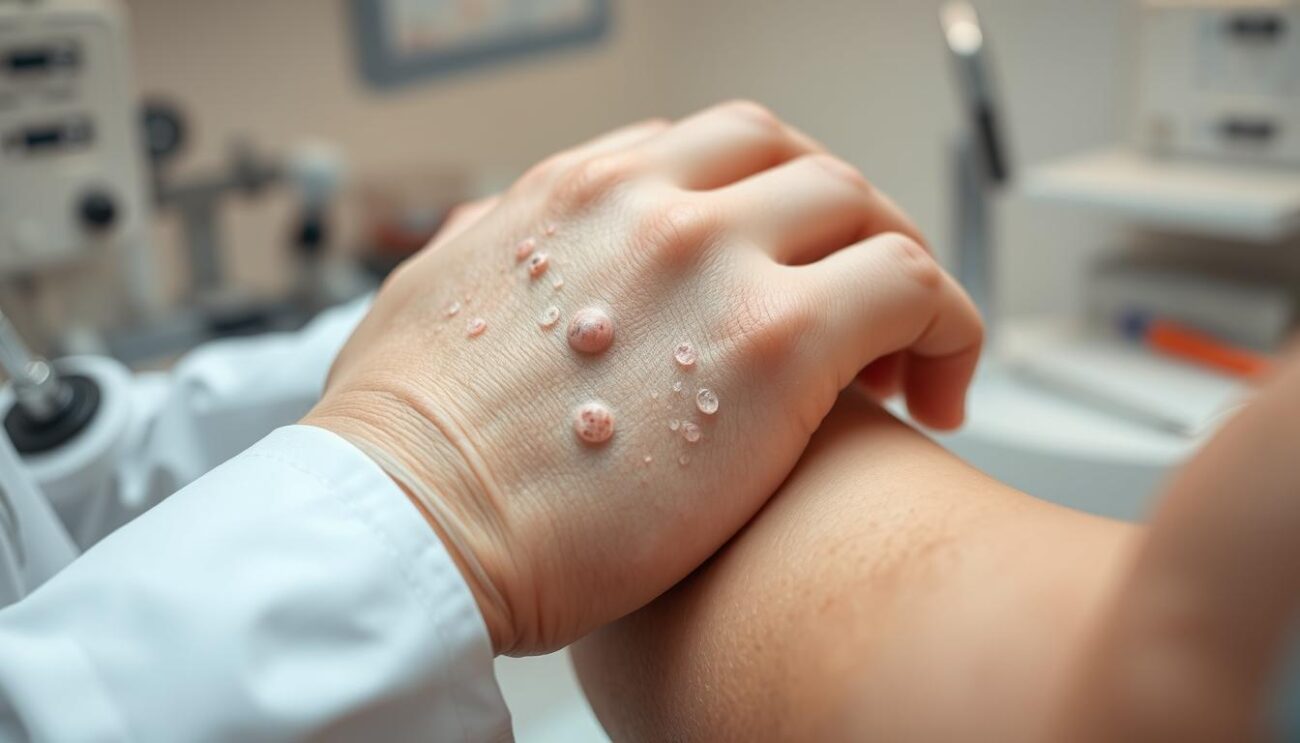
Treatment Options
Treating pustular psoriasis aims to ease symptoms and stop outbreaks. For mild, local cases, topical treatments like steroid creams and coal tar are often used first. But, for severe or widespread cases, other treatments are needed.
Phototherapy
Light therapy, or phototherapy, is a good option for pustular psoriasis. PUVA and narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB) can manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. You’ll need to visit a doctor for 6-8 weeks to see results.
Oral Medications
For severe or hard-to-treat cases, oral medications like cyclosporine and methotrexate are used. These drugs calm down the immune system. But, they can have side effects, so a doctor’s watch is key.
Biologic Therapies
New biologic therapies target pustular psoriasis. These injectables, like IL-17 inhibitors, aim at specific inflammation pathways. They’re great for severe or hard-to-treat cases.
| Treatment Option | Mechanism of Action | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Treatments | Reduce inflammation and promote skin cell turnover | Convenient, often the first-line therapy for mild cases | May take several weeks to show noticeable effects |
| Phototherapy | Exposure to controlled doses of UV radiation | Can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups | Requires regular visits to a medical facility |
| Oral Medications | Suppress the overactive immune response | Effective for more severe or treatment-resistant cases | Can have significant side effects, require close monitoring |
| Biologic Therapies | Target specific inflammatory pathways | Highly effective for managing severe or recalcitrant cases | May require injection and long-term treatment |
The right treatment for pustular psoriasis depends on the case’s type and severity. Your medical history and how you react to treatments also matter. A doctor will help choose the best way to manage your symptoms and outbreaks.
Managing Pustular Psoriasis
Dealing with pustular psoriasis flare-ups can be tough. But, there are ways to manage it well. Making lifestyle changes and managing stress are key to keeping your skin healthy.
Lifestyle Changes
People with pustular psoriasis should use gentle, fragrance-free skin care products. This helps avoid more irritation. Also, try to avoid things that might trigger flare-ups, like harsh chemicals or extreme weather.
Quitting smoking is also important. Smoking can make pustular psoriasis worse.
Stress Management
Stress can make pustular psoriasis worse. Doing things that reduce stress, like exercise or yoga, can help. Getting help from mental health experts is also a good idea.
By changing your lifestyle and managing stress, you can help control your pustular psoriasis. This improves your life quality.
“Effectively managing pustular psoriasis requires a holistic approach, addressing both medical treatments and lifestyle factors. By making informed choices and seeking support, individuals can better navigate the challenges of this condition.”
Complications and Outlook
Pustular psoriasis is a severe condition that can lead to serious complications if not treated. The widespread, inflamed skin increases the risk of infections. It also affects the quality of life for those who have it.
Research shows that psoriasis, especially the generalized pustular form (GPP), can cause serious issues like multi-organ failure.Inflammatory skin conditions like psoriasis are linked to many health problems. These include heart issues, liver disease, kidney problems, mental health issues, and even Alzheimer’s disease.
- Pustular psoriasis raises the risk of infections because of the damaged skin barrier and inflammation.
- The severity of pustular psoriasis can greatly impact an individual’s quality of life. It affects daily activities, social life, and emotional health.
- People with pustular psoriasis are also at a higher risk of developing other conditions. These include heart disease, arthritis, and mental health disorders.
| Potential Complications | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Events | Increased Risk [30,31,32] |
| Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) | Increased Risk [33] |
| Renal Impairment | Increased Risk [34] |
| Mental Health Disorders | Increased Risk [30,31] |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Increased Risk [30] |
But, with proper medical management and a comprehensive treatment plan, many manage their symptoms well. They reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks. Ongoing research into pustular psoriasis may lead to better treatments. This could improve the prognosis for those with this condition.
“Pustular psoriasis is a severe and unpredictable form of the disease that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. Early and effective treatment is crucial to manage the condition and prevent potential complications.”
Living with Pustular Psoriasis
Dealing with pustular psoriasis can be tough, both in body and mind. Finding good ways to cope and getting the right help is key. It helps you live better with this condition.
Coping Strategies
People with pustular psoriasis can use many ways to handle their symptoms:
- Try stress-reducing activities like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to lessen flare-ups.
- Use a gentle, fragrance-free skincare routine to care for your skin.
- Stay away from things that make symptoms worse, like too much sun or irritants.
- Keep a healthy lifestyle with a good diet, exercise, and enough water to help your body.
Support Resources
There are many resources to help those with pustular psoriasis:
- Join patient support groups for a community, shared stories, and emotional support.
- See mental health experts for help with the emotional side of the condition.
- Look into advocacy groups for education, help with laws, and navigating healthcare.
- Use online forums and websites for reliable info, treatment ideas, and managing tips.
By using coping strategies and getting support, people with pustular psoriasis can manage their condition better. This makes their daily life easier and improves their overall health.
“With the right support and coping mechanisms, living with pustular psoriasis can be more manageable and less isolating.” – Jane Doe, Psoriasis Advocate
Conclusion
Pustular psoriasis is a severe and rare skin condition. It can greatly affect a person’s life. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing it.
These treatments include topical creams, light therapy, oral drugs, and biologic therapies. They help reduce complications and improve life quality.
Despite challenges in tracking its prevalence, research is making progress. Healthcare teams and scientists are working together. This collaboration is crucial for understanding and treating pustular psoriasis.
Early treatment is vital. It can greatly improve outcomes and lessen the condition’s impact. This is why early diagnosis and treatment are so important.
Research in pustular psoriasis is ongoing. New diagnostic methods and treatments are being developed. These advancements offer hope for those affected.
By staying informed and seeking support, people with pustular psoriasis can manage their health better. This helps improve their overall quality of life.