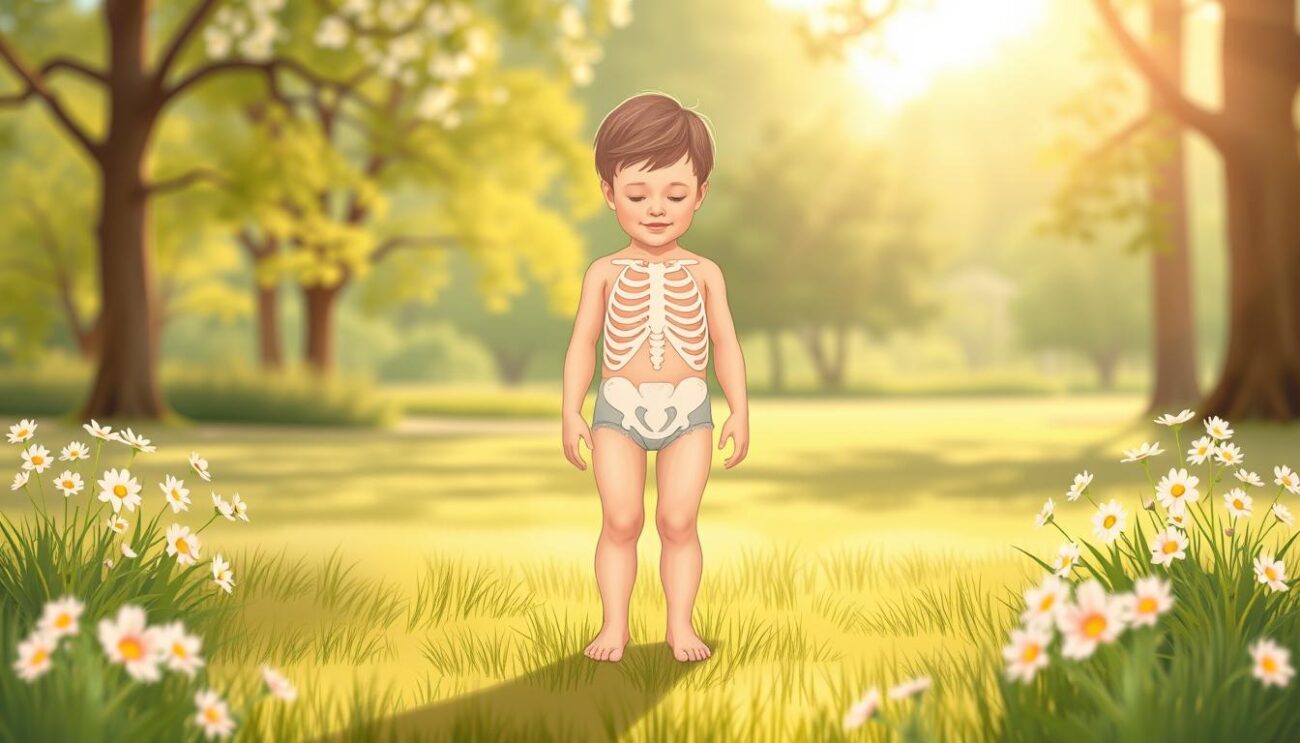
Did you know a simple nutritional lack can cause rickets? This problem affects bone health, especially in kids. But, treating it is surprisingly easy. Learn how to make bones strong and healthy again and avoid rickets’ bad effects.
Key Takeaways
- Rickets is mainly caused by not enough vitamin D and calcium, making bones soft and weak.
- Good treatment means fixing these nutritional gaps with supplements and better diet.
- In serious cases, you might need braces or surgery to fix bone shapes.
- It’s important to watch how kids grow to keep bones healthy and stop rickets from coming back.
- Preventing rickets is possible with enough vitamin D and sunlight.
Understanding Rickets: Causes and Symptoms
Rickets mainly affects children and is caused by a lack of important nutrients for bone growth. The main issue is not enough vitamin D and calcium. Vitamin D helps the body use calcium, which is key for strong bones.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Vitamin D and Calcium
Without enough vitamin D and calcium, bones don’t mineralize right. This leads to the bone deformities seen in rickets. Places with less sun have more rickets because there’s less vitamin D from sunlight. Dark-skinned people also face a higher risk because their bodies make less vitamin D from sunlight.
Signs of Rickets in Children
- Bowed legs
- Softening of the skull
- Enlargement of the wrists and ankles
- Delayed closure of the soft spots on the head
- Delayed growth and motor skill development
- Bone pain and muscle weakness
Rickets can cause serious problems like an abnormally curved spine and seizures. In some cases, surgery is needed. Finding and treating rickets early is key to avoiding lasting bone problems and ensuring kids grow up with strong bones.
| Cause | Impact | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D Deficiency | Impaired calcium absorption, leading to soft and weakened bones | Adequate sun exposure, vitamin D-rich diet, and supplements as needed |
| Calcium Deficiency | Insufficient mineral content for proper bone mineralization | Calcium-rich diet, including dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods |
Diagnosis: Identifying Rickets
Diagnosing rickets involves a detailed check-up. This includes a physical exam and several tests. Doctors play a key role in finding the cause and how severe it is.
Physical Examination
The doctor will closely look at the child’s bones and growth. They check the skull, legs, chest, wrists, and ankles. They look for signs of bone problems, like deformities and widening.
Imaging Tests and Blood Work
X-rays are used to see bone health. They show bone deformities and growth issues. Blood and urine tests check for vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus levels. These are key for bone growth.
A detailed physical examination and diagnostic tests help doctors diagnose rickets. They then create a treatment plan to fix the problem and improve bone health.
“Rickets primarily occurs in growing children before the fusion of the epiphyses, affecting areas like wrists, knees, and costochondral junctions.”
Rickets Treatment: Nutritional Interventions
The main way to treat rickets is by fixing nutritional gaps through supplements and diet changes. This helps fix bone mineralization issues.
Vitamin D and Calcium Supplements
Vitamin D and calcium supplements are often given to those with rickets. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and keeps bones healthy. Getting enough calcium is also key for strong bones. These supplements help improve bone health and stop rickets from getting worse.
Dietary Changes for Better Bone Health
Changing what you eat can also help treat rickets. Eating foods high in vitamin D, like fatty fish and egg yolks, boosts vitamin D levels. Foods rich in calcium, such as dairy and leafy greens, also support bone health. Combining these diet changes with supplements offers a full treatment plan for rickets.
| Nutrient | Rich Food Sources | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified dairy products | 400-600 IU for children |
| Calcium | Dairy products, leafy greens, beans | 700-1,300 mg for children |
Many studies show that nutrition plays a big role in treating rickets. A Turkish study found vitamin D supplements cut rickets risk by 96% in kids under three. A Chinese study showed a mix of vitamin D, calcium, and nutrition advice lowered rickets risk by 24% in the same age group.
“Proper nutrition, including adequate vitamin D and calcium intake, is essential for maintaining bone health and preventing the development of rickets.”
– Professor Jatinder Bhatia, MBBS, FAAP
Lifestyle Modifications for Rickets Management
Changing your lifestyle can help manage rickets, along with good nutrition. Getting more sunlight helps your body make vitamin D. This vitamin is key for strong bones. Also, doing outdoor play and weight-bearing exercises boosts bone health and overall health.
Sunlight Exposure and Outdoor Activity
Rickets often comes from not enough vitamin D. This can be fixed by getting more sunlight. Kids with rickets should go outside, especially at midday when the sun is strongest. This helps make vitamin D, which is vital for bones.
- Children with rickets should get 15-30 minutes of sun a day, a few times a week.
- Play, walk, or do sports to get vitamin D and strengthen bones.
- Wear clothes that cover you and use sunscreen to protect from the sun while still getting vitamin D.
By making these lifestyle changes, people with rickets can improve their bone health. These changes work well with the right food to manage rickets.
“Exposure to sunlight is a key factor in the prevention and treatment of rickets, as it allows the body to produce its own vitamin D.”
| Lifestyle Factor | Benefit for Rickets Management |
|---|---|
| Sunlight Exposure | Promotes vitamin D production, essential for calcium absorption and bone mineralization |
| Outdoor Activity | Encourages weight-bearing exercise, strengthens bones, and supports overall physical well-being |
Bracing and Surgical Options for Severe Cases
Some severe cases of rickets need more than just diet changes and lifestyle tweaks. When bone deformities are too far gone, doctors might suggest bracing or surgery. These methods aim to fix the bones and help them grow right.
Bracing for Bone Alignment
Bracing is key for severe rickets. It supports and positions the bones, helping them grow straight. This is especially helpful for kids with big leg or spine curves. It keeps their bones on the right path for growth and function.
Surgical Correction of Bone Deformities
For the worst cases of rickets, surgery might be the only option. Orthopedic surgeons can fix the bones by realigning, reshaping, or stabilizing them. This is for kids whose bones haven’t improved with diet and lifestyle changes.
| Treatment | Indication | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bracing | Moderate to severe bone deformities | Guides bone growth, improves alignment |
| Surgery | Severe, persistent bone deformities | Corrects significant skeletal abnormalities |
Bracing and surgery are for the most severe rickets cases. They’re used when diet and lifestyle changes don’t work. The goal is to align and stabilize the bones for proper growth in children with this condition.
Monitoring Growth and Development
Effective treatment of rickets needs ongoing monitoring and care adjustments. Doctors will regularly check the child’s growth and development. They use X-rays and blood tests to track treatment progress and adjust supplements as needed. This ensures the child’s bones develop correctly and any issues are quickly handled.
Regular Check-ups and Adjustments
During treatment, the child will have regular check-ups to monitor their rickets monitoring and bone health. At these appointments, the healthcare team will:
- Measure the child’s height, weight, and other growth indicators
- Perform physical examinations to assess bone deformities and joint mobility
- Conduct imaging tests, such as X-rays, to evaluate bone mineralization and structure
- Order blood tests to analyze levels of vitamin D, calcium, phosphorus, and other key nutrients
- Adjust the treatment adjustments plan as needed, including modifying supplement doses or adding new therapies
By closely monitoring growth and development, the healthcare team can ensure the child’s bones are responding well to treatment. They make any necessary regular check-ups to optimize care.
| Monitoring Parameter | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Height and weight measurements | Every 3-6 months |
| Bone X-rays | Every 6-12 months |
| Blood tests (vitamin D, calcium, phosphorus) | Every 3-6 months |
| Physical examinations | Every visit |
By closely monitoring the child’s growth and development and making timely treatment adjustments, healthcare providers can ensure the best possible outcomes for children with rickets.
Preventing Rickets: A Proactive Approach
Preventing rickets starts with good nutrition for mom and baby. Moms-to-be need enough vitamin D and calcium for baby’s bones. After birth, keeping vitamin D levels up in babies helps avoid rickets.
Prenatal and Infant Nutrition
A study by Thacher et al. (2016) gave global advice on stopping rickets. They stressed the role of prenatal nutrition. They found a link between mom’s vitamin D deficiency and rickets in kids.
Healthcare experts should teach parents about good infant nutrition. They should talk about the benefits of breastfeeding or formula with vitamin D and calcium. This helps keep kids’ bones strong and stops rickets.
Maintaining Adequate Vitamin D Levels
It’s key to keep vitamin D levels right to stop rickets. Maiya et al. (2008) showed vitamin D deficiency can cause serious heart problems in babies. Regular sun exposure and vitamin D supplements help, as Wheeler et al. (2015) found in New Zealand.
By taking these steps, parents and doctors can help keep kids’ bones healthy. This lowers the chance of rickets.
Rickets Treatment: Addressing Underlying Conditions
Rickets can be a sign of a deeper health issue, like a genetic disorder or trouble absorbing vitamins and minerals. In these cases, the main rickets treatment is to fix the underlying problem. This might involve special medical care, more tests, and specific treatments.
Genetic forms of rickets need a mix of phosphate supplements and a certain vitamin D treatment. These plans are key to managing the condition and helping bones grow strong.
Conditions like celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or kidney disorders can make it hard for the body to take in important nutrients. This raises the risk of rickets. So, it’s important to treat these conditions to manage rickets symptoms.
Regular health checks, especially for babies and kids, can spot nutritional deficiencies early. This can stop rickets or other problems from starting. With the right treatment, most kids with rickets can fully recover and grow normally.
“Adequate exposure to sunlight is crucial for the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin, which is essential for preventing rickets.”
By tackling the root causes of rickets, doctors can create rickets treatment plans. These plans not only treat symptoms but also prevent future problems. They help keep bones healthy and support overall health.
Genetic Forms of Rickets and Specialized Care
Rickets is often linked to poor nutrition, but some genetic conditions can also cause it. Genetic forms of rickets need special care and treatment plans to tackle the genetic issues.
Hypophosphatemic rickets is caused by a genetic defect that messes with how the kidneys and bones handle phosphate. To manage this, a mix of phosphate supplements and a specific vitamin D treatment might be needed to keep bones healthy and strong.
Other genetic rickets types, like hereditary rickets, also need specialized care and custom treatment plans. These diseases can be tricky to diagnose and might need a team of experts, including pediatric endocrinologists, geneticists, and orthopedic specialists.
Getting a proper diagnosis and starting treatment early is key for kids with genetic rickets. Genetic tests and personalized treatment plans can help avoid serious problems like skeletal deformities and growth issues. With the help of a team of experts, families can make sure their kids get the care they need for healthy bones and growth.
Conclusion: Promoting Bone Health and Well-being
Treating rickets well means fixing the nutritional gaps, changing lifestyles, and sometimes using braces or surgery. Knowing the causes, signs, and treatments helps doctors and caregivers. They can then improve bone health and prevent problems.
It’s key to feed babies and pregnant women right to lower rickets risk. The Healthy People 2010 goal is to boost health and life quality. It also aims to end health gaps, showing why bone health matters.
Every year, 1.5 million people in the U.S. break bones due to osteoporosis. Over 10 million have bone diseases. So, treating and preventing rickets is more urgent than ever. By focusing on bone health, we can make a better future for everyone.



