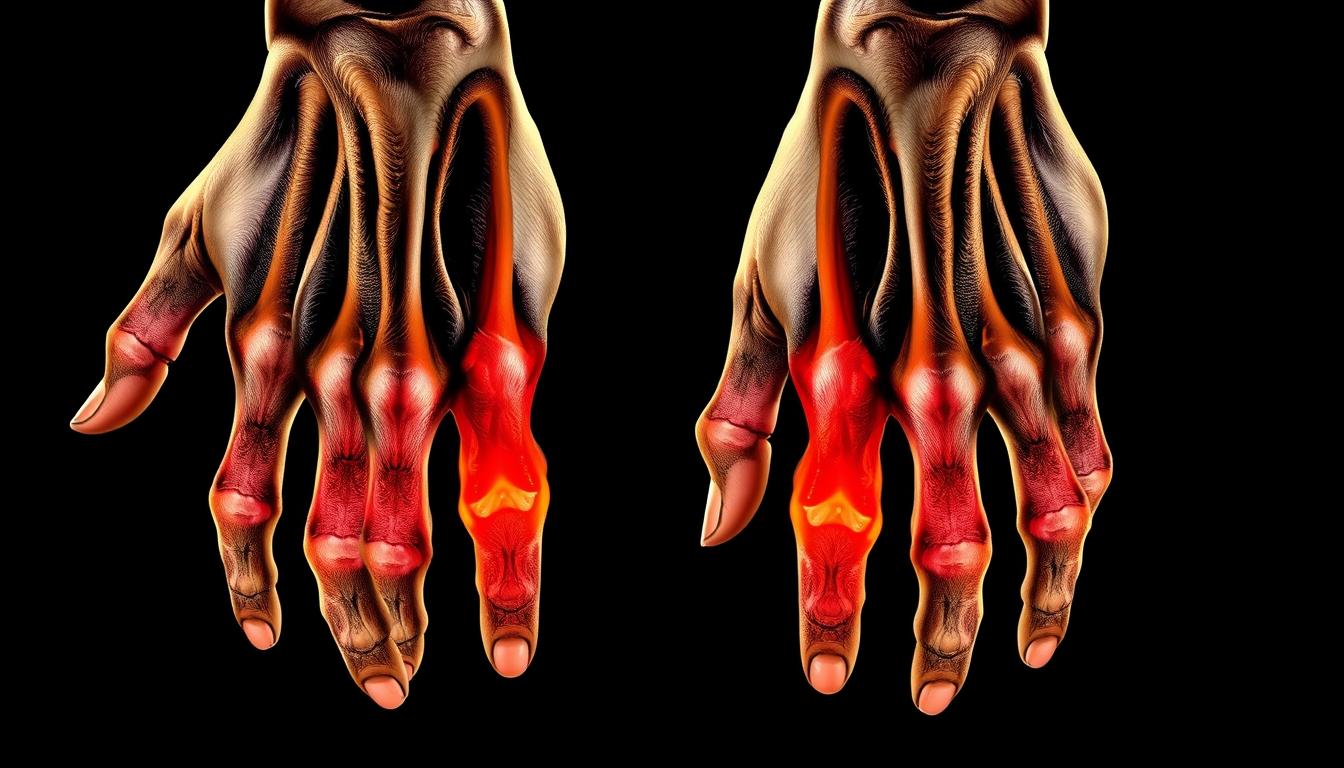
Do you have ongoing joint pain, swelling, and stiffness? These could be signs of rheumatoid arthritis. It’s an autoimmune disease where the body attacks the lining of joints. This condition can cause a lot of pain and damage to joints if not treated.
Knowing the causes and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is key. It’s the first step to managing and finding relief.
Key Takeaways
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes joint inflammation and damage.
- Common symptoms include pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness in small joints like fingers and toes, as well as larger joints like knees and shoulders.
- The disease can also affect other parts of the body, including the eyes, heart, and lungs.
- Women are more susceptible to developing rheumatoid arthritis, which typically appears in middle age.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to manage the condition and prevent permanent joint damage.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition where the body attacks its own joints. This attack causes inflammation, swelling, and pain, mainly in hands, wrists, and feet. If not treated, it can lead to permanent damage.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Autoimmune Condition
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s healthy tissues. This leads to inflammation in the synovium, causing the symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The main symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Joint pain, tenderness, and swelling, especially in the small joints of the fingers and toes
- Morning stiffness that can last for an hour or more
- Decreased range of motion in the affected joints
- Fatigue, fever, and other systemic effects
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary and come and go. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing the disease and preventing damage.
| Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Joint Pain and Swelling | The primary symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are joint pain, tenderness, and swelling, often in the small joints of the hands and feet. |
| Morning Stiffness | Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis typically experience prolonged morning stiffness, which can last for an hour or more. |
| Decreased Range of Motion | The inflammation and swelling in the joints can lead to a decreased range of motion and difficulty with everyday tasks. |
| Systemic Effects | Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause fatigue, fever, and other systemic effects as the immune system attacks the body. |
It’s important to note that the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary from person to person. The condition can have periods of flare-ups and remissions, making it a challenging and unpredictable disease to manage.
Early Signs and Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition. It can be hard to spot in its early stages. The early signs of rheumatoid arthritis include tenderness, pain, and swelling in small joints. These symptoms often appear and disappear, making it tough to diagnose.
As RA gets worse, inflammation damages cartilage and bone in the joints. This leads to less movement and visible deformities. There are four main stages of rheumatoid arthritis:
- Stage 1 (Early Inflammation): Characterized by joint pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Stage 2 (Cartilage Damage): Ongoing inflammation leads to the deterioration of cartilage within the joints.
- Stage 3 (Bone Damage): The inflammation progresses, causing damage to the underlying bone structures.
- Stage 4 (Severe, Irreversible Joint Damage): Advanced joint damage and deformities, often accompanied by decreased mobility and chronic fatigue.
Early treatment and management are key to slowing RA’s progression. Regular check-ups with a rheumatologist are vital. They help patients manage RA and improve their quality of life.
“The progression of RA varies based on factors such as family history, age at diagnosis, disease triggers, antibodies in the blood, and smoking habits.”
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is still a mystery. Researchers think it’s a mix of genetics and environment. Some people are more likely to get it because of their genes. Things like infections, stress, and toxins can start the immune system’s attack.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Rheumatoid arthritis has a strong genetic link. Studies show certain genes make people more likely to get it. For example, about half of those with rheumatoid arthritis have a specific antibody in their blood.
Things like smoking and being overweight can also increase the risk. These are things we can change.
Immune System Malfunction
The main problem in rheumatoid arthritis is the immune system gone wrong. Instead of protecting us, it attacks our joints. This leads to pain, swelling, and damage.
| Rheumatoid Arthritis Causes | Key Facts |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors |
|
| Environmental Factors |
|
| Immune System Malfunction |
|
In summary, rheumatoid arthritis comes from a mix of genetics and environment. This mix leads to the immune system attacking the body. This causes joint inflammation and damage.
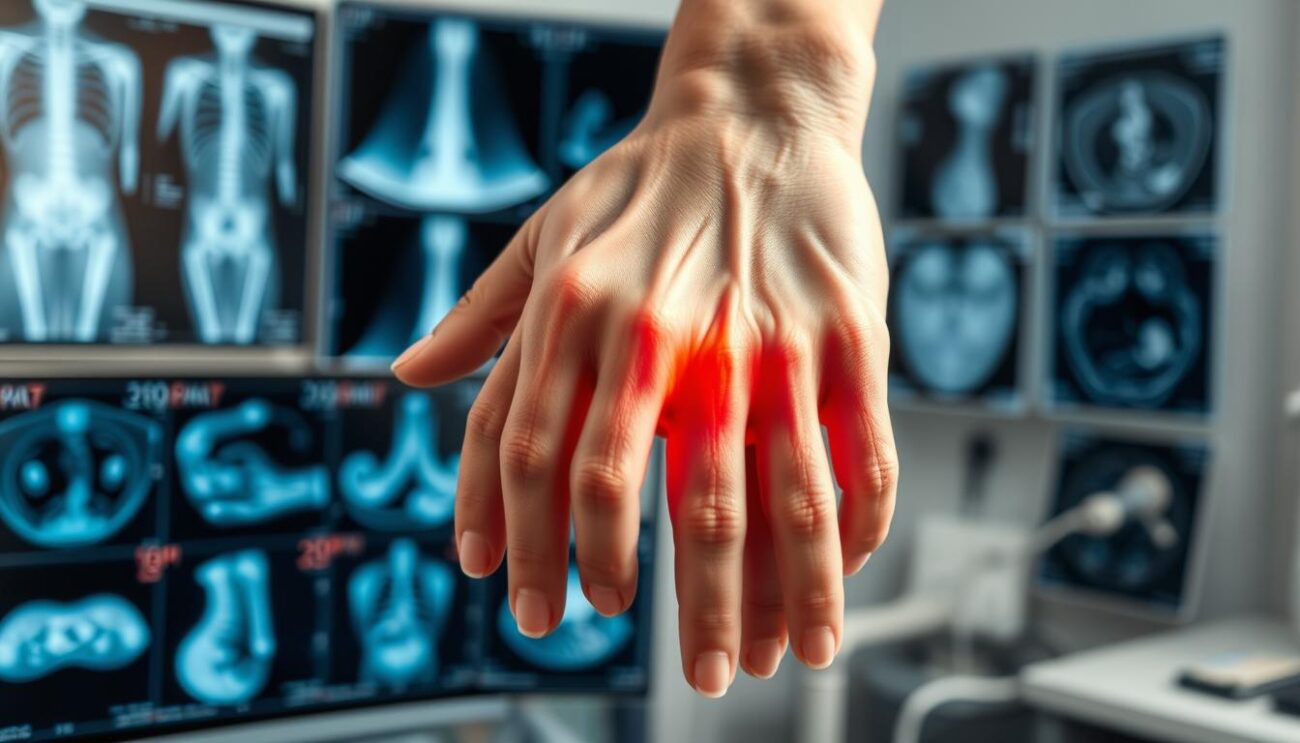
Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis involves a detailed medical check-up. This includes a thorough history, physical exam, and tests. The goal is to find the cause of joint pain and swelling.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The doctor will ask about your joint symptoms and how long you’ve had them. They’ll also ask about your family history and if you smoke. They’ll check for joint tenderness, swelling, and limited movement.
Blood Tests and Imaging
The doctor may run blood tests to check for inflammation. They’ll look for signs like high ESR or CRP levels. They might also test for autoantibodies like rheumatoid factor and ACPAs.
Imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans can show joint damage. This helps the doctor decide on the best treatment.
Getting a correct rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis early is key. It lets doctors start treatment quickly. This can greatly improve your health and prevent serious problems later.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Managing rheumatoid arthritis needs a mix of medicines, therapies, and lifestyle changes. The main goals are to cut down inflammation, ease symptoms, stop damage to joints and organs, and boost function and well-being.
Medications and Therapies
For rheumatoid arthritis treatment, doctors often use a mix of medicines. This includes disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and corticosteroids. Methotrexate is usually the first DMARD given. Biologics like Adalimumab (Humira) and Etanercept (Enbrel) are used when DMARDs don’t work well. Steroids like hydrocortisone and methylprednisolone are recommended for severe rheumatoid arthritis or during flare-ups.
Physical and occupational therapy are key in rheumatoid arthritis management. They help keep patients mobile, strong, and able to do daily tasks. In serious cases, surgery like joint replacement for hips and knees may be needed to improve mobility and ease pain.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diet, Exercise, and Lifestyle
Living a healthy lifestyle can also help manage rheumatoid arthritis. Eating a balanced rheumatoid arthritis diet full of anti-inflammatory foods can help. Regular exercise is also good, as it strengthens muscles, improves joint function, and boosts overall health.
“75% of people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) benefit from working with a physical therapist to create a strength and mobility program.”
Managing stress and quitting smoking are also key. Smoking can make rheumatoid arthritis worse. By treating the condition and taking care of oneself, people with rheumatoid arthritis can manage their condition better and live a better life.
Complications and Effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects more than just the joints. The ongoing inflammation can harm other organs, causing various complications. These can greatly impact a person’s health and well-being.
Untreated RA can shorten a person’s life by 3-10 years. It also increases the risk of organ damage and early death. This is a serious concern for those living with RA.
RA’s inflammation can spread beyond the joints, affecting other parts of the body. This can lead to issues like pleurisy, pulmonary fibrosis, pericarditis, and myocarditis. These problems can harm the lungs, heart, and surrounding tissues. RA can also cause vision-related issues like cataracts, dry eye syndrome, and scleritis.
The medications for RA can harm organs like the liver and kidneys. They may also weaken the immune system, raising the risk of infections. RA is also linked to mental health concerns, such as depression and anxiety. These can worsen the condition’s symptoms and quality of life.
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect various parts of the body, including the hands, elbows, wrists, ankles, toes, hips, jaw, knees, neck, and shoulders. It can also impact the voice-related joints, leading to speech and communication challenges.
Early and effective treatment is key to managing RA and preventing complications. Healthcare providers can help control inflammation and joint damage. This helps patients maintain their quality of life and reduces the long-term effects of RA.
Difference Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Arthritis Types
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a unique autoimmune disorder. It differs from other common arthritis types like osteoarthritis and gout. While they all cause joint pain and inflammation, their causes and characteristics are different.
Osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear over time. This leads to cartilage loss and bone friction, causing pain and stiffness. In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition. It occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation and damage.
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by uric acid crystals in the joints. It usually affects one joint, like the big toe, causing sudden, intense pain and swelling. Unlike rheumatoid arthritis, which can affect many joints, gout is typically limited to one joint.
| Characteristic | Rheumatoid Arthritis | Osteoarthritis | Gout |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause | Autoimmune disorder | Wear and tear | Uric acid crystal buildup |
| Joint Involvement | Multiple joints, often symmetrical | Individual joints | Single joint, typically the big toe |
| Pain and Stiffness | Worse in the morning, fluctuates throughout the day | Worse at the end of the day after activity | Sudden, intense pain and swelling |
| Treatment Approach | Immune-modulating medications, physical therapy | Weight management, exercise, pain medication | Anti-inflammatory drugs, dietary changes |
It’s important to know the differences between rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout. This helps in getting the right diagnosis and treatment. Early and proper treatment can greatly improve the lives of those with arthritis.
Coping with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can be tough, but the right strategies can help. Keeping a positive mindset is key. It helps manage the emotional side of RA.
Having a strong support network is also important. Connecting with others who get RA helps you feel less alone. Support groups, both in-person and online, offer valuable rheumatoid arthritis coping and rheumatoid arthritis support.
Stress-reducing activities like meditation and deep breathing can help. They ease the physical and emotional pain of RA. These practices boost mental health and help the body heal.
Creating a rheumatoid arthritis lifestyle that focuses on self-care is crucial. Eating well, exercising gently, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking are important. Adding nutrients like omega-3s and curcumin can also help.
| Coping Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Positive Mindset | Manages emotional impact, enhances well-being |
| Strong Support Network | Provides community, valuable insights, and shared experiences |
| Stress-Reducing Techniques | Promotes mental well-being, supports natural healing |
| Balanced Diet and Regular Exercise | Helps manage symptoms, improves overall health |
| Supplements (e.g., Omega-3s, Curcumin) | May provide additional relief for joint pain and inflammation |
By using these strategies, people with RA can manage their condition. They can keep a fulfilling rheumatoid arthritis lifestyle. With the right support and care, living with RA can be rewarding.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune condition that can greatly affect a person’s life. There is no cure yet, but research and treatments have improved. Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment are key to managing it. This includes medication, physical therapy, and making lifestyle changes.
The study of rheumatoid arthritis is ongoing, especially in developing countries. Research and updates to treatment guidelines help shape how we manage this condition. This includes the EULAR recommendations for managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Understanding the genetic, environmental, and immunological factors of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial. This knowledge helps us develop more personalized and effective treatments. By taking a comprehensive approach, we can improve the lives of those with rheumatoid arthritis.